What is sunburn?
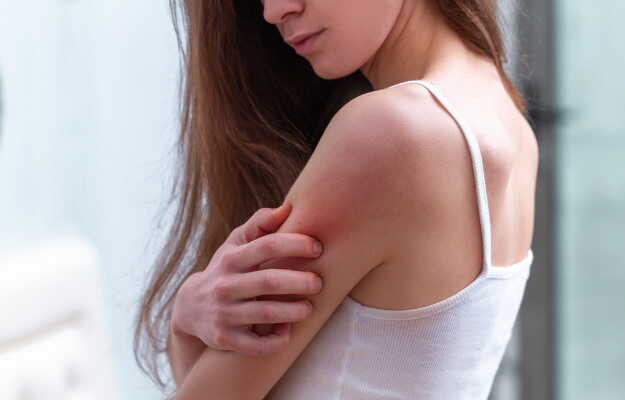
Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays of the sun can cause reddening and inflammation on the skin surface leading to a condition called sunburn. It is more common in individuals who are exposed to the sun for longer periods of time.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
- The first sign of sunburn is redness with itching.
- This is accompanied by pain, discomfort, and burning sensation on the affected area.
- Often, you may develop blisters and oedema (swelling because of fluid accumulation) in the affected area.
- The blisters may be superficial or may be present in the underlying deeper layers of the skin. They are filled with water and are often painful.
- Other symptoms include fever, nausea and vomiting.
What are the main causes?
Sunburn is mainly caused due to prolonged exposure to UV radiation. Other than the sun, other sources of UV rays could be artificial lamps.
Risk factors include the following:
- Populations living in areas where the ozone layer is thin or depleted are also at high risk of developing sunburn.
- Children and older adults are more susceptible to sunburn as compared to the middle-aged and adolescent population.
- Those with a lighter skin tone are at greater risk of developing sunburn, as they have limited capacity to withstand the exposure due to lack of melanin in their skin.
- Rarely, a genetic condition predisposes a person to develop sunburn. This condition is called xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Sunburn risk is also greater with certain medications like sulfa drugs, diphenhydramine, promethazine, amitriptyline and others.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
- Sunburn is a clinically obvious condition, therefore, diagnosis mainly involves distinguishing it from other skin conditions like allergies, photo-allergies, and photo-toxicity reactions.
- Most sunburns heal spontaneously within a few weeks, if exposure to the sun is terminated.
- Anti-inflammatory medicines help to relieve the inflammation and pain. Drugs like aspirin may also be prescribed.
- To soothe the redness, moisturising creams, gels, and cool showers are recommended.
- The patient is advised to be adequately hydrated, as sunburn draws a good amount of water from the skin.

 Doctors for Sunburn
Doctors for Sunburn  OTC Medicines for Sunburn
OTC Medicines for Sunburn

 Home Remedies for Sunburn
Home Remedies for Sunburn