RCT is a multi-step procedure and usually requires more than one visit to your dentist. It can be done by a general dentist as well as an endodontist (a dentist with specialization in root canal therapies). Following is the stepwise procedure for your root canal treatment:
History
Your dentist will take a detailed history of your current health status to avoid any emergency during treatment. The dentist may ask you the following questions:
- Blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Whether you are currently suffering from breathing problems, heart diseases, liver diseases, kidney diseases, mental disorders etc.
- Past or current experience of seizures, tuberculosis (TB) or any other recent infection, blood disorders, problems in blood clotting etc.
- Any known allergic reactions to medicines.
- If you are currently taking any medicines.
- Past surgeries and any complications related to them
- Any other dental treatment that you might have undergone in the past.
Note: If you have high blood pressure, high blood sugar, had heart surgery (pacemaker insertion, prosthetic valve, heart defects, or heart transplant), had tuberculosis in the past, undergone or undergoing treatment for blood thinning, your dentist may not start the procedure till your physician gives clearance in writing that it is safe for you to undergo this treatment.
Hence, it is important for you to inform your dentist about all the medications that you are on in order to prevent any complication during treatment.
This is because certain medicines and ongoing treatments may cause disruption or hindrances in dental procedures such as RCTs.
X-ray
Your dentist might either advise or take an X-ray of the affected tooth in the clinic itself before starting the procedure. This will help in understanding the condition of the tooth and evaluating the extent of infection in the surrounding jaw bone.
Anesthesia
If you have never received anesthesia in the past, your dentist may do a small test on your forearm to check whether you are allergic to it. Anesthesia is given to make your tooth numb while your dentist is carrying out the procedure. This makes the procedure painless and comfortable for you as well as for your dentist. Within a few minutes, you may experience numbness or tingling sensation in your lip, tongue, and face on the same side where the injection is given. There is nothing to worry about. This happens because of the fact that one nerve supplies to many structures on the same side. Hence, numbing one part in the middle will also make other areas numb. Sometimes, when the pulp is dead, you may not even require anesthesia.
Isolation of the tooth
In this procedure, your dentist will keep your tooth dry and isolated from the rest of your mouth using cotton rolls or a rubber sheet known as rubber dam. This will prevent any further contamination of the canals with saliva while cleaning and filling them.
Access opening
It is the next step after isolating your tooth. Your dentist will use a powered instrument with water spray to make way through the hard tissues of your tooth to the tooth pulp. This will take out all the damaged portions of your crown. Hence, it will not only help in accessing all the root canals in your tooth roots, but it will also prevent the transfer of infection in deeper areas. After this step, your dentist might use a hand instrument to remove the upper wider part of the pulp from the crown portion of your tooth.
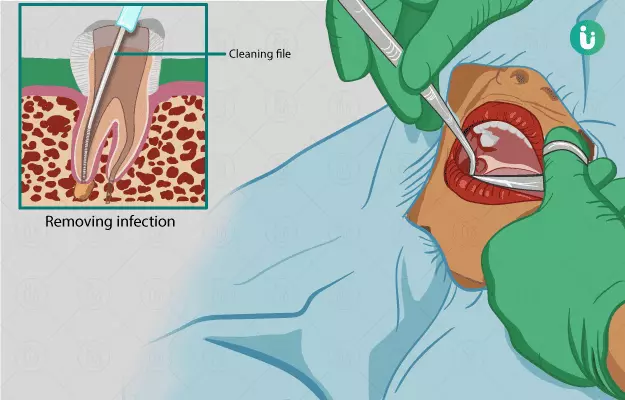
Cleaning and shaping of the root canals
Cleaning is done in order to take out the infected tooth pulp from your narrow canals. Dentists use various types of needle-like instruments which have cutting edges for this procedure. These are known as files and the technique is known as filing. These files have stoppers to prevent slipping of the file beyond the expected length of your tooth root. Files can be used manually (hand-operated) or with a powered device. They engage the tooth pulp and the underlying affected hard tissue and remove it from narrow areas of the canals. Once it is done, these files are used with increasing diameter to shape your canals. The length of each root is identified either by taking an X-ray with files in all the canals or by using an apex (the tip of a root) locator (a device which locates the apex and tells the root length). Shaping is important to make your canals more accessible and easily fillable.
Disinfection
This is a very important step in root canal treatment. Your dentist will wash your root canals every once in a while with sterile (germ-free) water and with disinfecting chemicals. It is of utmost importance that all the debris flows out of your root canals and isn’t further pushed down towards the bone while filing.
Medicaments
The above procedures are done on your first visit to the dentist. After cleaning and shaping, your dentist might fill your canals with an antibiotic paste (intracanal medicaments) to kill the remaining bacteria as well as to prevent their spread till you come for your next visit. Over this paste, they will put an antiseptic-soaked cotton and a temporary white filling. This temporary filling will prevent the entry of bacteria from saliva in your root canals. It is advised that you do not drink anything for one hour after leaving the clinic. You are also advised not to chew anything from the treated side for the next 24 hours. Between your first and second visit, your dentist may prescribe and advise you to take some antibiotics and painkillers to make the infection, pain and the swelling to subside.
Filling (Obturation) of root canals
In permanent adult teeth
On your second visit, your dentist will take out the temporary filling, the cotton, and the antibiotic paste from your canals. After cleaning them, your dentist will do a final assessment to check if there are signs of bleeding or any pus discharge. If there are bleeding and pus discharge, you may have to come for a third visit for final treatment after taking the medicines prescribed on the second visit.
If the root canals are free of blood and pus, your dentist will give a final wash to the tooth and its canals, take an X-ray with a cone (conical-shaped filling material) in each root canal to ensure that the filling will not fall short. After washing, small tube-like rolled papers (paper points) are used to dry the canals completely. A paste which seals the filling material with the inner surface of the root canal (a sealant) is applied. After the sealant is applied, your dentist will fill all the root canals with the filling (obturating) material. Thereafter, a permanent filling is placed in the crown portion of your tooth. The height of the tooth is slightly reduced so that it does not come in contact with the opposite tooth. This prevents the application of chewing forces on the treated tooth and helps it heal faster.
In milk teeth
Milk teeth are filled with a filling material which is available in paste form. The paste comes in injection-like tubes. These make it easier to fill the root canals of the baby teeth. Over this paste, a permanent filling material is placed. The paste sets and hardens over a period of time.
Emergency access opening
This is a very painful condition in which you might experience severe pain in the tooth, with or without associated swelling in the same area. This happens when there is severe inflammation (swelling) of your tooth pulp which causes pressure to build up in your tooth. Since a tooth has an outer hard structure, there is no place for the swelling to expand and it results in severe pain. In such a case, rush to your dentist, or a nearby dentist immediately. The dentist will give an injection on the affected side to make the area numb and will perform an access opening of the affected tooth. This procedure is slightly painful because the action of anesthesia is not as strong when there is a swelling or pus associated with the affected tooth. However, getting an access opening done will release the pressure and relieve your pain. The dentist will prescribe antibiotics and painkillers to make the symptoms subside. Later on, you will have to get your root canal treatment completed to prevent further spread of infection.
X