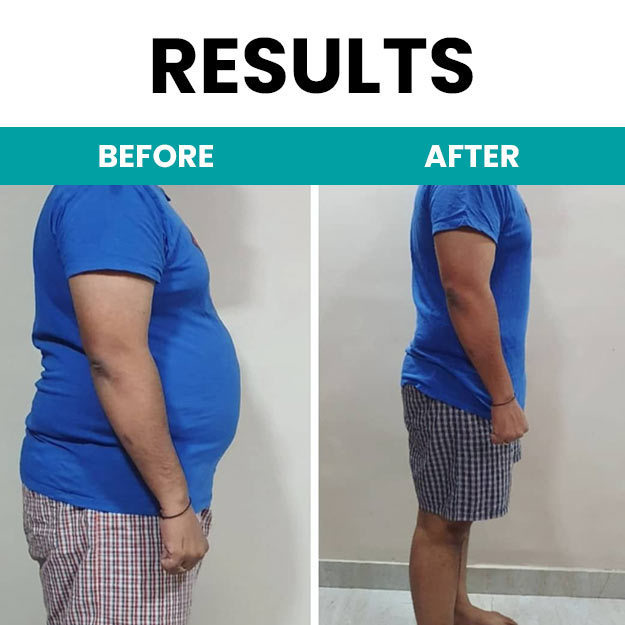
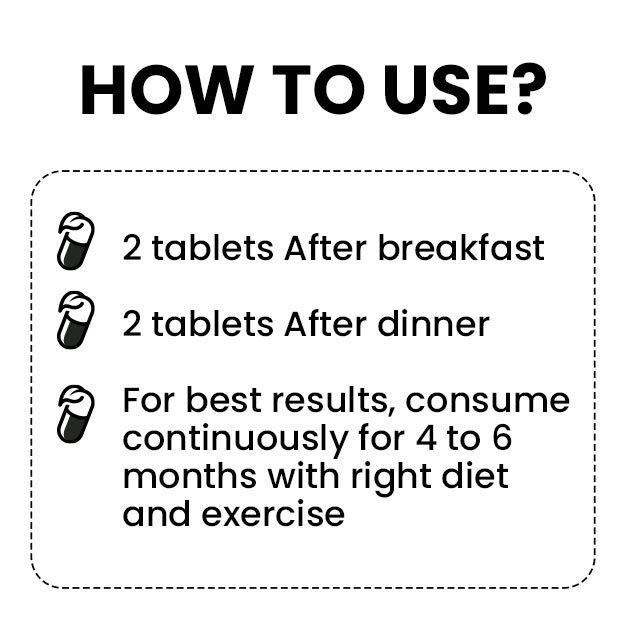
Our bodies are constantly working to keep up the various processes and organs working at optimum efficiency. A lot of us may have heard the term metabolism, even used it at certain occasions, either to boast how good your metabolism is or to complain about slow it is. But do you know what exactly metabolism is?
Metabolism is the sum total of all the processes going on in your body. It includes the basic functions like energy generation, digestion, elimination, detoxification and all the other processes that are needed to keep you up and running. Various metabolic pathways are constantly active at the cellular level to generate molecules and compounds needed to feed the cellular machinery. They also aid in the transport of nutrients to different parts of the body. Looks a lot more complex this way, doesn’t it?
Let’s make it a bit easier and break down metabolic processes:
- Catabolism: Catabolism refers to the process of breaking down of complex compounds into simpler ones, like sugars are broken down into carbohydrates and proteins into amino acids, similarly fats are broken down into fatty acids. Catabolic reactions provide energy for the body.
- Anabolism: Anabolism refers to the processes that buildup smaller molecules into more complex compounds. This includes converting amino acids into proteins. These reactions take up the energy which is produced by catabolism and serve to build up body tissues and new cellular structures.