A cyst is a pathological sac-like cavity that may contain something solid, liquid or gaseous. It does not contain pus. Cysts can appear anywhere in the body.
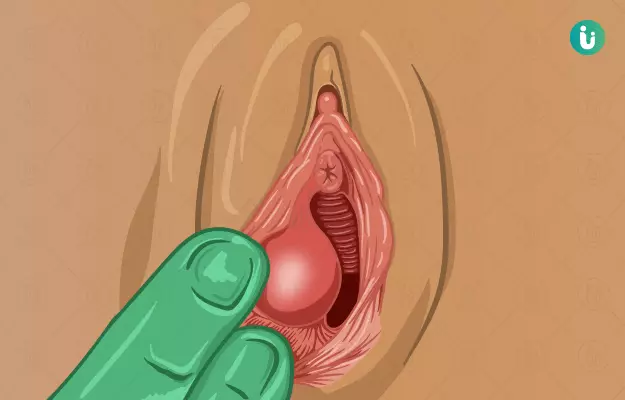
Vaginal cysts are usually painless, round lumps. Their size can range from the size of a pea to that of a plum.
Vaginal cysts are usually seen due to trauma to the vaginal tissue during childbirth. They can also occur due to blockage in one of the two Bartholin duct openings (these ducts normally open on either side of the vagina.)
Though most cases of vaginal cysts are asymptomatic, some of the most common symptoms involve pain while urinating, pain during sex and vaginal bleeding.
Vaginal cysts can be diagnosed with the help of ultrasound, pelvic exam and biopsy.
The treatment of the cyst is done either by draining the cyst or by removing it surgically. If the cyst is small in size, it can be managed by soaking the lower half of the body in warm water, to help the cyst rupture and drain.