What is syphilis?
Syphilis is a contagious disease that is mainly passed on through the sexual route. Sometimes, it can also be passed on through close physical contact.
It may remain latent in a person for a long time, making them the carriers of the infection. Syphilis is bacterial in origin.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Syphilis occurs in three distinct stages, each with specific symptoms.
-
Primary syphilis:
- It is an incipient stage seen until 3 months of the infection.
- A person develops small painless ulcers, without any other major symptoms.
- Primary syphilis heals well in a few weeks, even without intervention.
-
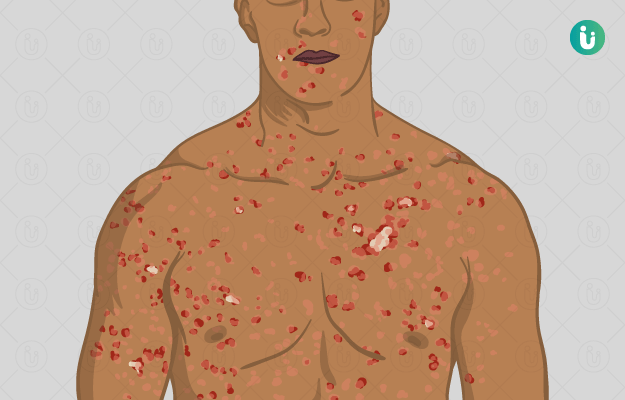
Secondary syphilis:
-
Tertiary syphilis:
- It is the advanced stage where major organs are affected.
- Blindness, paralysis and cardiac problems are the major concerns during this stage.
- If untreated, it may become fatal.
What are the main causes?
- The bacterium that causes syphilis is Treponema pallidum.
- Having unprotected sex is the most common mode of transmission of this infection.
- Homosexual men are at a higher risk of developing syphilis.
- An infected woman can also pass on the infection to her newborn, which is called congenital syphilis.
- Contact with an exposed rash or sore can also transmit the infection to the person.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis of syphilis:
- Before running tests, the doctor will take your sexual history and examine the skin, particularly the genital area.
- If the symptoms and examination point towards syphilis, a blood test is conducted, along with an examination of the sore, to check for the syphilis bacteria.
- If tertiary syphilis is suspected, tests are run to check the status of individual organs.
- Fluid is collected from the spinal cord and examined for bacteria to detect nervous system involvement.
- If syphilis is confirmed, the partner is also advised to get tested.
Treatment of syphilis:
- Antibiotics are prescribed for early syphilis, usually as injectable antibiotics. Penicillin is a commonly used antibiotic for the treatment of syphilis.
- In tertiary syphilis, extensive treatment is required, mainly for improving the symptoms since the organism cannot be completely eliminated at this stage.
- It is important to abstain from any sexual activity or close physical contact throughout the treatment period.

 Doctors for Syphilis
Doctors for Syphilis  OTC Medicines for Syphilis
OTC Medicines for Syphilis
 Syphilis articles
Syphilis articles
 Homeopathic Treatment of Syphilis
Homeopathic Treatment of Syphilis





 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria











