Summary
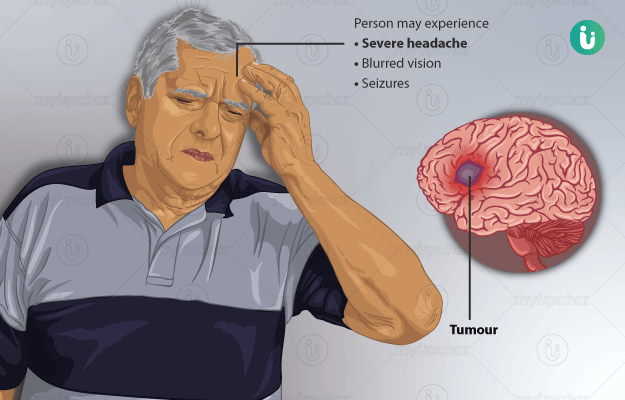
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of the cells of the brain. Tumors can be harmless (benign) or cancer-causing (malignant). Brain tumors that form within the brain are called primary brain tumors. Secondary brain tumors or metastatic brain tumors, on the other hand, are tumors caused by cancer originating in some other part of the body that then move to the brain. The signs and symptoms of a brain tumor depend on various factors such as the size of the tumor, the speed at which the tumor grows in size and the area where the tumor is located. Some early and common symptoms of brain tumors include changing headache patterns, frequent and severe headaches, problems with speech, and difficulty in balancing. Treatment of a brain tumor depends on the type of brain tumor as well as the size and location of the tumor.

 Doctors for Brain Tumour
Doctors for Brain Tumour  OTC Medicines for Brain Tumour
OTC Medicines for Brain Tumour
 Brain Tumour articles
Brain Tumour articles
 Diet for Brain Tumour
Diet for Brain Tumour
 Homeopathic Treatment of Brain Tumour
Homeopathic Treatment of Brain Tumour




































 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra

 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria