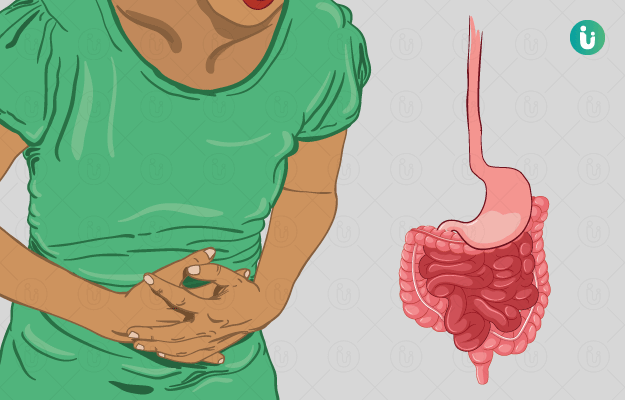
What are digestive disorders?
Diseases related to the digestive tract including organs such as the stomach, small intestine and colon as well as the liver, gallbladder, biliary tract and pancreas are collectively termed digestive disorders or gastrointestinal disorders. These disorders encompass a wide range of diseases, such as pancreatitis, constipation, diarrhoea, Crohn’s disease, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), heartburn, gallstones, colitis, ulcers, hernia and the list goes on.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Some common symptoms are warning signs of the whole range of digestive disorders:
- Bloating and passing of gas
- Constipation
- Diarrhoea
- Blood in stool
- Heartburn
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain in the stomach
- Problems in swallowing
- Weight gain or loss
- Changes in bowel habits
What are the main causes?
Digestive disorders can be due to one or many of the causes given below:
Common causes:
- Microbial infection
- Inflammation in the GIT
- Deficiency of digestive enzymes
- Poor blood circulation to the intestine
- Formation of gallstones
- Side effects of anti-inflammatory drugs
- Stress
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol
- Excessive intake of fat
- Spicy food
- Genetic causes: Expression of certain genes can be a cause of diseases like pancreatitis, liver diseases and Crohn’s disease.
- Post-surgical causes: Surgeries involving removal of gallbladder or resection of a part of the bowel can result in digestive diseases.
- Presence of autoimmune inflammatory and chronic diseases: Diseases like Sjogren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) can lead to digestive disorders. Some diseases like cancer of liver, colon and pancreas can affect digestion.
- Age: Increasing age can lead to weakening of digestive system.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Digestive disorders can affect a single organ or multiple organs in the digestive system. The three basic pillars of diagnosis are medical history, physical examination and laboratory tests.
- Medical history: Knowing your eating habits, lifestyle and bowel habits, and a psychological evaluation, can help your doctor decide further testing.
- Physical examination: Abdominal examination by hand and stethoscope can detect abnormalities in your abdomen.
- Laboratory tests:
- Stool examination
- Endoscopy
- Intubation of GIT
- Laparoscopic examination
- Abdominal fluid testing
- Tests for acid reflux
- Imaging techniques such as normal and barium X-rays of GIT, and MRI and CT scan of abdomen
- Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen
The treatment will depend on the diagnosis of the disease. The following strategies can make the treatment successful:
- Identify your trigger factors: You may focus on certain foods and habits which worsen your digestive problem. With proper advice from your doctor and dietician, you can overcome the problem.
- Medication: Anti-diarrhoeal, anti-nausea, anti-emetic and antibiotics can be prescribed depending upon your symptoms.
- Surgery: You may be recommended surgical intervention for disorders like gallstones, appendicitis and hernia.
- Endoscopy: For gastrointestinal bleeding, endoscopic delivery of haemostatic drugs can be given.
Although these treatments are available to relieve you from digestive disorders, some simple lifestyle changes can act as preventive measures:
- Exercise
- Yoga and meditation
- Hygienic eating habits, fixed eating routine
- Use of probiotics to replenish your gut flora
Digestive disorders are preventable with minor changes in your daily routine and eating habits. Medication and surgical intervention can treat the disorders completely in most. It is always better to consult your physicians before opting for any alternative therapy.

 Doctors for Digestive Disorders
Doctors for Digestive Disorders  OTC Medicines for Digestive Disorders
OTC Medicines for Digestive Disorders