What is folliculitis?
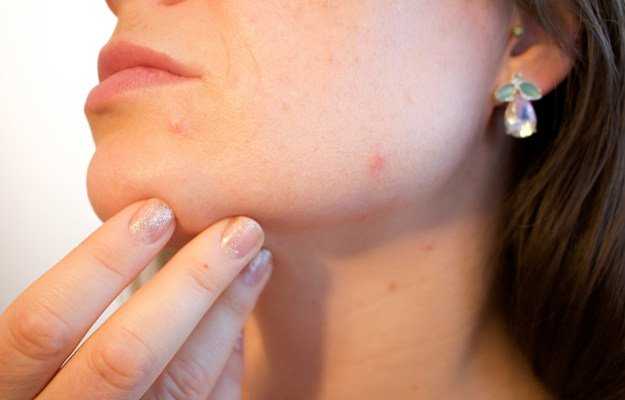
Folliculitis is a common skin infection that affects the hair follicles. The infection can occur anywhere on the skin or the scalp. Normally, it is seen in areas with terminal hair growth like the head and neck region, axillae (armpit), groin, and buttocks. It looks similar to an acne breakout but with a red ring around the lesion indicating infection.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Folliculitis shows varied symptoms like itching of the skin, pain at the site or it may be asymptomatic at times. Following is the list of symptoms of folliculitis –
- Red bumps or white-headed pimples are seen in clusters near the hair follicle.
- Pus-filled blisters which break open.
- Itching and burning of surrounding skin.
- Tenderness of the skin.
- Swollen bump or mass on the skin.
What are its main causes?
Folliculitis is mostly caused by the infection of the hair follicles due to bacteria, fungus, virus, or irritation due to certain chemicals.
- Staphylococcal folliculitis is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterial infection occurs usually without fever.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes hot tub folliculitis, which occurs due to improperly sanitised bathtubs.
- Gram negative folliculitis is rare and occurs due to antibiotic treatment.
- Pityrosporum ovale causes acne-like skin rash on the back and the chest of adults, resulting in pityrosporum folliculitis.
- Tinea capitis or ringworm of the scalp causes a fungal infection of the hair follicles.
- Herpes simplex virus causes recurrent localised facial folliculitis in men who shave with a razor.
- Chronic friction that occurs on shaving in the opposite direction of hair growth causes mechanical folliculitis.
- Occlusion folliculitis occurs when ointment or creams or moisturisers block the growth of the hair follicle leading to inflammation.
- Certain chemicals like coal tars and excess use of corticosteroids also cause folliculitis.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Your doctor will examine the infected area of the skin thoroughly and take your medical history. The doctor may also use dermoscopy for microscopic examination of the infected skin sample. If the response to the treatment is not good, then a swab test is done to check for the cause of infection. A skin biopsy may be needed in chronic cases.
As per the cause of folliculitis, topical antifungal or antibiotic creams, ointments, and shampoo are prescribed. Minor surgery is performed to excise a large boil or carbuncle. Infection of the follicle can be cleared by using laser therapy.
Application of warm moist cloth over the area can soothe discomfort. Washing of the area twice daily with antibacterial soap may prevent persistent or recurrent folliculitis.

 OTC Medicines for Folliculitis
OTC Medicines for Folliculitis