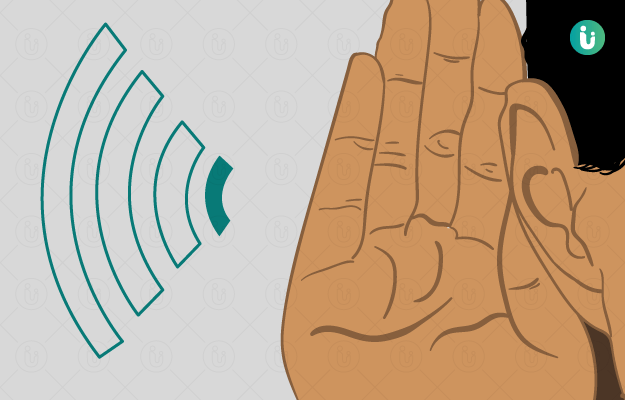
What is hearing loss?
Hearing loss is defined as the reduced ability to hear sounds which can affect one or both the ears. Based on the inability to hear, hearing loss can be classified a mild, moderate and severe. Very little to no hearing is called deafness. The condition can be permanent or temporary depending on the cause.
According to WHO, by the year 2050, there will be more than 90 million people throughout the world with hearing disability. India is amongst the regions with a higher prevalence of hearing loss.
What are its main associated signs and symptoms?
Hearing loss itself is a symptom. Signs that indicate a hearing loss includes:
- Struggle hearing while in a noisy setting
- Poor response during a conversation
- Listening to music or watching television at high volumes
- Repetitively asking others the same thing
What are its main causes?
Hearing loss is commonly seen in the elderly due to the natural ageing process, which results in degeneration of cells. You may start experiencing difficulty in hearing from age 40 onwards.
Hearing disability in children can be caused by various factors such as:
- Genetics
- Infection during pregnancy
- Certain medications taken during pregnancy
- Jaundice within 1 month of birth
- Low birth weight
- Deprivation of oxygen at birth
Other causes that can affect the hearing include:
- Diseases like meningitis, measles, mumps
- Infections of the ear
- Medications
- Head or ear injury
- Earwax
- Exposure to noises at the workplace or recreational settings (concerts, nightclubs, party) including using headphones or earphones at high volumes
How is it diagnosed and treated?
If you think you have a hearing problem, consult your doctor (an audiologist). Your doctor will find the cause of your hearing loss and finalise the management plan. If earwax is found to be the cause, removing the earwax will help improve hearing loss.
The doctor may also suggest the use of hearing aids or implants if required. If hearing loss cannot be treated, learning lip reading and sign language can improve your communication with others.
Hearing loss in children can be prevented by:
- Vaccinating against measles and mumps
- Screening for infections like otitis media
- Not listening to loud noises/music
- Taking care that children do not insert objects into their ears
Adults working in a noisy workplace should use ear protection.

 Doctors for Hearing Loss
Doctors for Hearing Loss  OTC Medicines for Hearing Loss
OTC Medicines for Hearing Loss
 Hearing Loss articles
Hearing Loss articles
 Homeopathic Treatment of Hearing Loss
Homeopathic Treatment of Hearing Loss







 Dr. Ajay Mohan (AIIMS)
Dr. Ajay Mohan (AIIMS)

 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria