What is Hepatitis C?
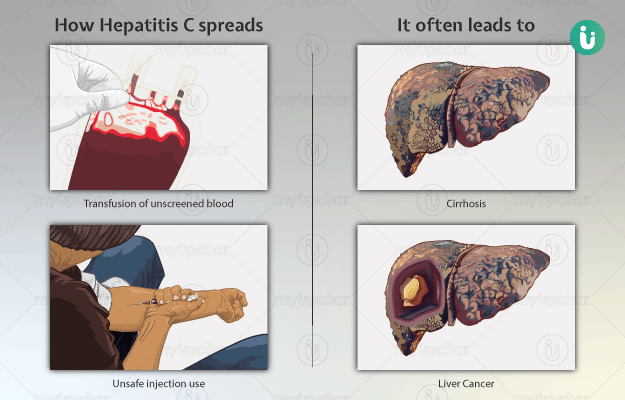
Hepatitis C refers to the inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The primary mode of transmission is through blood. The disease develops as an acute infection and progresses to chronic in 80% of the affected. The acute infection lasts for a maximum of 6 months and recovery is possible without any treatment while the chronic infection lasts for a longer duration and may lead to cirrhosis and carcinoma (cancer).
Based on the genotype, HCV is classified into 6 types ranging from 1 to 6. Genotype 3 is the most commonly reported in India followed by genotype 1. Identification of genotype is necessary to provide appropriate treatment.
According to WHO, the prevalence of HCV infection in the Indian subcontinent is 0.5 - 1% against 1.6% worldwide and proves as a threat to the population.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Acute phase
Time usually taken for your symptoms to appear varies from 2 weeks to 6 months. 80% of infected individuals are asymptomatic but may experience:
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Reduced appetite
- Yellow discolouration of the eyes and the skin
- Abdominal discomfort
Chronic phase
In later stages, there is:
- Fluid accumulation in the abdomen and associated bacterial infection
- Bleeding in stools or in the vomit
- Dark stools
- Difficulty in breathing
- Pain in joints
What are the main causes?
HCV is mainly transmitted by blood through the following ways:
- Sharing of needles and personal products like razors in drug users
- Usage of infected needles and syringes in hospitals
- Inappropriate sterilization of medical equipment
- Blood transfusion with contaminated blood
Other modes of transmission are:
- Sexual route
- Mother to baby
Infection doesn’t spread through contaminated food and water nor by sharing household items.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
If you experience the mentioned symptoms, consult your doctor and he/she may recommend blood tests to determine the level of liver enzymes along with HCV antibody (Anti -HCV) and HCV ribonucleic acid (HCV RNA) tests to detect the virus. This test can detect the virus within just a week.
Liver biopsy is done to identify the extent of liver damage. HCV genotype testing is also carried out prior to initiation of therapy.
Direct acting antivirals are the newest drugs available for the treatment of hepatitis C infection with a treatment duration of 3 months. Due to the unaffordable nature of newer agents in India, conventional therapy is still used widely.
Currently, no vaccination is available for prevention of infection, but the disease can be prevented to a great extent by reducing the exposure to the virus (avoiding needle and syringe sharing, blood transfusion and sexual contact with affected individuals).
Proper adherence to the medication given by your doctor can help overcome the infection and improve your quality of life.

 Doctors for Hepatitis C
Doctors for Hepatitis C  OTC Medicines for Hepatitis C
OTC Medicines for Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C FAQs
Hepatitis C FAQs Hepatitis C articles
Hepatitis C articles News for Hepatitis C
News for Hepatitis C
 Diet for Hepatitis C
Diet for Hepatitis C












 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra

 Dr. Ajay Mohan (AIIMS)
Dr. Ajay Mohan (AIIMS)