What is muscle weakness?
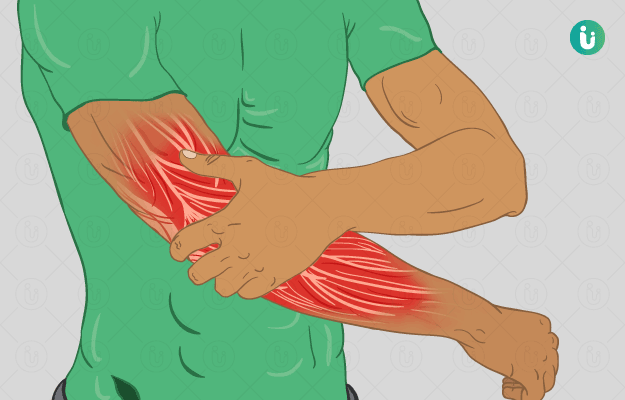
Muscle weakness is the reduced ability of your muscles to perform normal activities. It is simply the lack of strength of a muscle to do a particular action. Muscle weakness can be temporary, for example, muscle weakness experienced after strenuous exercise returns to normal after rest. However, a persistent weakness of muscles without an apparent cause can be due to some underlying serious condition. Nevertheless, muscle weakness is different from fatigue.
What are its main associated signs and symptoms?
Muscle weakness may show the following associated signs:
- Loss of strength of muscle to hold an object.
- Numbness or loss of sensations.
- Difficulty to move limbs, stand, walk or sit upright.
- Inability to move facial muscles or speak.
- Difficulty in breathing.
- Loss of consciousness.
What are the main causes?
There can be several underlying causes of muscle weakness. They are as follows:
- Muscular dystrophy
- Stroke
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Nerve damage
- Accident or injury
- Muscle inflammation
- Polio
- Myasthenia gravis
- Grave’s disease
- Guillain- Barre syndrome
- Multiple sclerosis
- Some drugs and alcohol
- Depression
How is it diagnosed and treated?
It is necessary to distinguish fatigue from muscle weakness; fatigue is the failure to do the movement after repeated attempts, while muscle weakness is the inability to do the movement in the first attempt itself. Your doctor will take a complete medical history as a preliminary step to diagnosis, followed by a thorough physical examination. The common diagnostic tests are as follows:
- Motor activity testing.
- Lung and heart function evaluation.
- Blood investigation to check for the levels of vitamins, electrolytes and hormone levels.
- Electromyography to test nerve functioning.
- MRI and CT scans.
- Muscle biopsy.
The treatment modalities are as follows:
- Medications, such as vitamin supplements, pain-killers, anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressants drugs depending upon the underlying disease.
- Physiotherapy and electrotherapy to strengthen the muscles and improve mobility.
- Surgery in case of accident or injury.
Regular exercises under the supervision of a physiotherapist and a balanced diet rich in essential minerals and vitamins may help you regain the strength of your muscles. Please note that a correct diagnosis and prompt treatment is necessary, as the symptoms may indicate a serious health problem. So, seek advice from your doctor if the symptoms persist.

 Doctors for Muscle Weakness
Doctors for Muscle Weakness  OTC Medicines for Muscle Weakness
OTC Medicines for Muscle Weakness