What is a bed sore?
Bed sores or pressure sores are outbreaks on skin and tissues that appear over the bony areas due to constant pressure for a long period of time. It is primarily caused due to a reduction in blood circulation due to sitting or lying in the same position constantly. Most bed sore cases are reported in elderly aged over 70 years.
An Indian study shows that the prevalence of bed sores in hospital admitted patients is 4.94%. Early treatment is necessary to prevent severe damage to the skin.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
In the early stages, you may notice shiny, red blotches of skin on the areas under constant pressure e.g., buttocks and shoulder blades in bedridden patients. It can gradually lead to loss of the upper layer of skin (epidermis) and develops an ulcer.
When the pressure is on the tissue beneath the bone, swelling and reduced sensations are experienced on the skin. Eventually, it leads to infection and loss of tissue in that area.
What are its main causes?
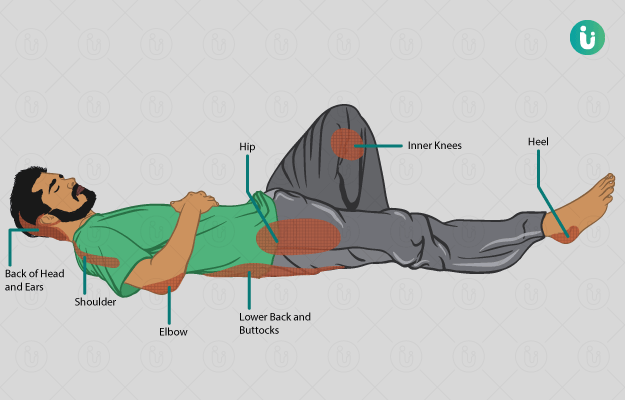
Bed sores develop when excessive and long-term pressure is applied on points like the back of shoulder, tailbone, buttocks and heels.
Applied pressure compresses the blood vessels which reduces the oxygen and nutrition supply to the skin. Lack of nutrients and oxygen for a long time causes the formation of ulcers.
Other causes of developing a bed sore includes:
- Shearing force, where the movement of skin and underlying tissue is in the opposite direction
- Friction injury
- Spinal cord injury
- Moisture which promotes bacterial growth and ulcer formation
- Conditions like dehydration, lack of nutrition, diabetes, heart diseases and obesity (in children)
- Lack of movement (e.g. paralysis, post operation)
- Cast use in fracture
How is it diagnosed and treated?
If you or your caretaker finds a bed sore on your body, inform your doctor immediately. Initial management includes thorough cleansing and wound dressing while changing the position of the patient to relieve the pressure on the area of the bed sore. Topical antibiotics will be advised in case of infection. Treatment duration lasts from 2 to 4 weeks depending on the severity of sores.
You can protect yourself from acquiring pressure sores by:
- Shifting your weight regularly while in a wheelchair
- Change your lying position while in bed
- Avoid friction injury like constant rubbing of skin against bed sheets
- Regular checking of your skin
- Skin cleansing with cleansing agents
- Keeping the skin in a dry state
- Adequate intake of water and healthy food

 Doctors for Bed (Pressure) Sores
Doctors for Bed (Pressure) Sores  OTC Medicines for Bed (Pressure) Sores
OTC Medicines for Bed (Pressure) Sores