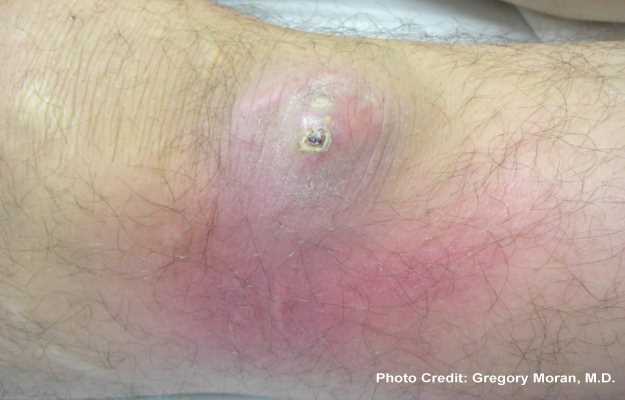
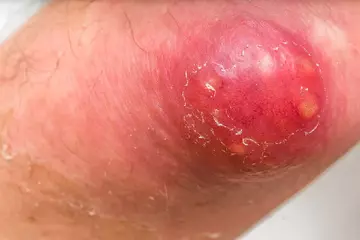
What is Sporotrichosis?
A long-standing fungal infection caused by the fungus sporothrix is known as sporotrichosis. Since this fungus lives in the soil of warmer climates and is often seen on plants like rose bushes, moss and hay, it is often called as the rose gardener’s disease. The fungal infection can develop on minor cuts or bruises on the skin. The infection most commonly affects farmers and garden workers.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Symptoms of sporotrichosis can occur anytime within the first 12 weeks of exposure of a cut or a wound to the fungus Sporothrix schenckii.
It first develops as a painless small red bump on the skin, which then forms an ulcer. When the fungus enters the respiratory system, it causes shortness of breath, cough, chest pain and fever.
There are two types of sporotrichosis: fixed and disseminated. Fixed sporotrichosis is confined to skin nodules only, whereas, disseminated sporotrichosis extends from the skin to other systems of the body. Patients with systemic diseases like diabetes mellitus, malignancies and AIDS are at a greater risk of developing disseminated sporotrichosis. Hence, arthritis, headaches and seizures are common symptoms of disseminated sporotrichosis.
What are the main causes?
Cutaneous sporotrichosis is caused by the fungus infecting the open wound or cut on the hands or arms of those handling the infected plants. Rarely, sporotrichosis infects the lungs as a result of inhaling the fungal spores. Immunosuppressed people are more likely to suffer from disseminated sporotrichosis since the infection spreads faster in them.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Your doctor can mostly diagnose sporotrichosis clinically simply by examination and taking a history. Collecting the pus sample from the nodule for culture and taking the sample of the infected skin for biopsy helps in confirming the diagnosis. Cutaneous sporotrichosis is mostly detected by blood tests. Though these infections are not life-threatening, they should be treated with antifungal medications like itraconazole. However, these medicines are not to be used in pregnancy. Intravenous injection of Amphotericin B is used to treat severe forms of sporotrichosis.
Thoroughly clean the wound and cover it to prevent any skin infection by the fungus entering the body through cuts. Also, you should avoid scratching of the wound to promote faster healing.