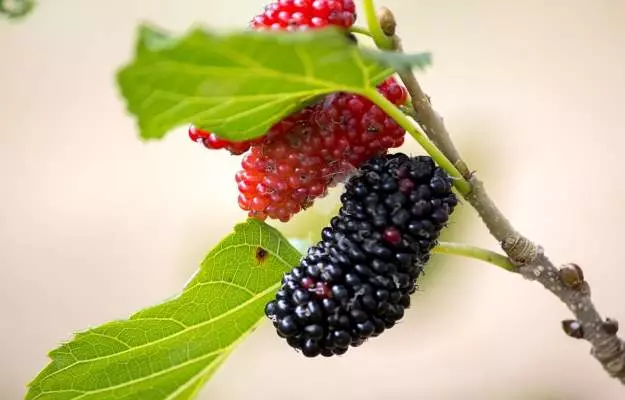
Mulberry, commonly known as morus, belongs to the family Moraceae. The plant grows in the wild but is also cultivated extensively for its various benefits. Mulberries are generally found in three colours - white, red, and black. The use of mulberry is widespread in Europe, the Middle East, Africa and the Indian subcontinent. Mulberries are also widespread in Greece, particularly in the Peloponnese, known as ‘Morea’ in the Middle Ages, from which the word ‘Morus’ has been derived.
Traditionally in Greece, mulberries were dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Minerva. In traditional Chinese herbal medicine, mulberries were used for centuries to treat heart diseases, diabetes, anaemia, and arthritis. It was also widely used in folk medicine, especially for the treatment of ringworm. In Ayurveda, mulberries have been used for the treatment of urine infection, intestinal worm infestations and skin infections.
Historically, mulberries are connected to the growth of the silk industry. In the Orient regions, mulberry leaves were used to fatten silkworms. The spread of mulberry trees across the world, thus, in a way, can be attributed to the need of mulberry leaves for the development of the silkworm industry.
Mulberries grow rapidly when young but they stop growing once they are about 10 to 15 metres. The mulberry bears multiple fruits, generally green or yellow when young turning red, black or white depending upon the species upon ripening and have a sweet flavour.
Some basic facts about mulberry (shahtoot)
- Botanical Name: Morus alba
- Family: Moraceae
- Common Name: Morus, mulberry
- Sanskrit Name: Shahtoot
- Parts Used: Fruits, leaves, barks
- Native Region and Geographical Distribution: Native to subtropical and temperate regions