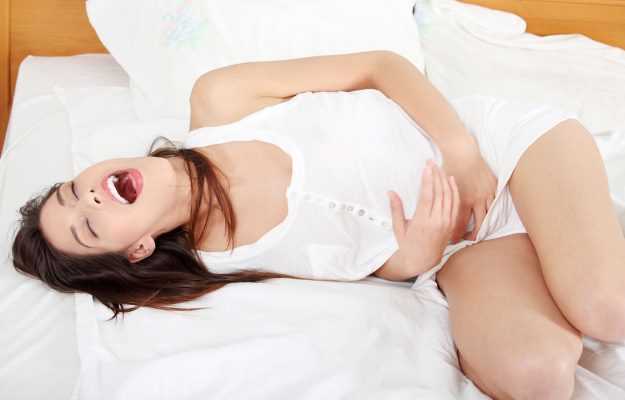
Dyspareunia is a condition where the woman experiences genital pain during sexual intercourse. It can deeply impact a woman’s quality of life.
Dyspareunia has a high prevalence rate, which can cause significant economic and health burden. Symptoms of dyspareunia often go unreported as many health professionals do not inquire about it or women never report it to the doctor due to social embarrassment. Pain during sex, though common, is an often neglected problem. It is seen in 3% to 18% of the global population.
Women experiencing dyspareunia feel emotionally isolated due to lack of support from their partner and family. Reports of pain during sex also result in different levels of interest during sex and sexual preferences. Such factors are strongly associated with difficult communication with one’s sexual partner. Insufficient foreplay, inadequate lubrication, and spasms are often linked with painful penetration. Sometimes, a pelvic or a speculum exam may increase the pain. Diagnosis is primarily clinical and made by a detailed history and physical examination. Imaging tests might be needed purely to rule out possible medical conditions leading to dyspareunia. Finding the physical and/or the psychological causes are necessary for appropriate treatment. Treatment involves seeking counselling with a psychologist or a sexual health counsellor, marriage counsellor, improving communication with the partner and treating the underlying physical causes.
Despite an increase in literacy rate, sex is still considered a taboo in India. Most people lack sexual knowledge and those suffering from such illnesses do not seek treatment. Every individual should lead a healthy sexual relationship with their partner, as it is one of the key aspects of any marriage or relationship.