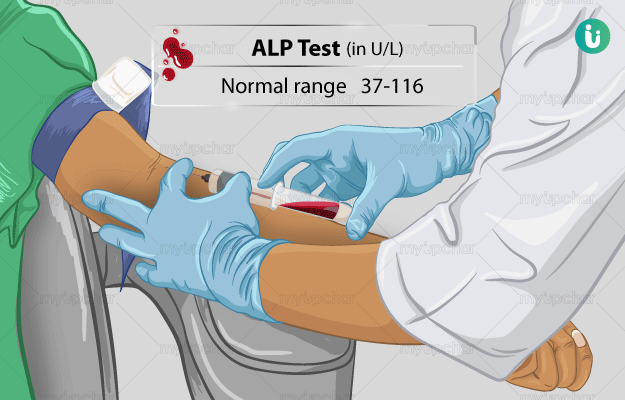
What is an Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) test?
An ALP test measures the levels of Alkaline Phosphatase or ALP enzyme in the blood. This enzyme is found throughout the body but predominantly in liver, bones, kidneys and biliary duct.
It is produced by the cells that help in the formation of bone, ie, osteoblasts. Different tissues produce different forms of ALP isoenzymes. These isoenzymes can be distinguished on the basis of clinical signs and symptoms or by performing a test, which also helps in determining if any isoenzymes is increased in the blood.
Few conditions that can increase the amount of ALP in the blood are increased and rapid bone growth, which mainly occurs during puberty; bone disorders, such as Paget’s disease or bone cancer; hyperparathyroidism (a condition that affects calcium in the blood); vitamin D deficiency; and damaged liver cells.
The alternate terms for this test are ALP, Alk Phos, Alkp, alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes and bone-specific ALP test.