What is a brain MRI?
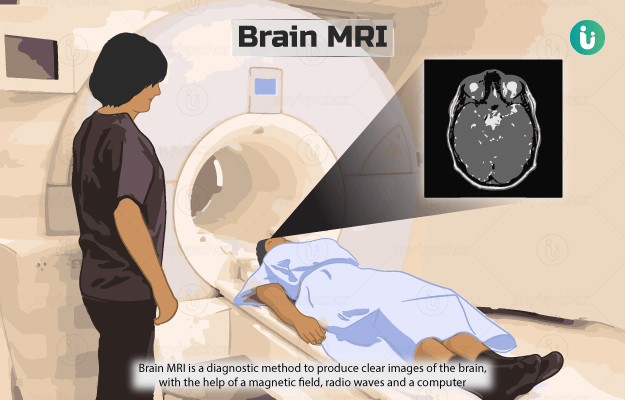
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is a diagnostic method to produce clear images of the brain, with the help of a magnetic field, radio waves and a computer.
During an MRI scan, a magnetic field is produced around the patient. The scanner then sends radio waves, which alter the alignment of atoms in their body. When the atoms realign, they send out radio signals that are picked up by the scanner and converted into images of the area examined. A contrast dye may be used to improve the quality of the images.
A brain MRI helps to detect problems in the brain. It is the most sensitive imaging test for the brain and can provide detailed images of areas in the brain that are not seen well on an x-ray or CT (computed tomography) scan.