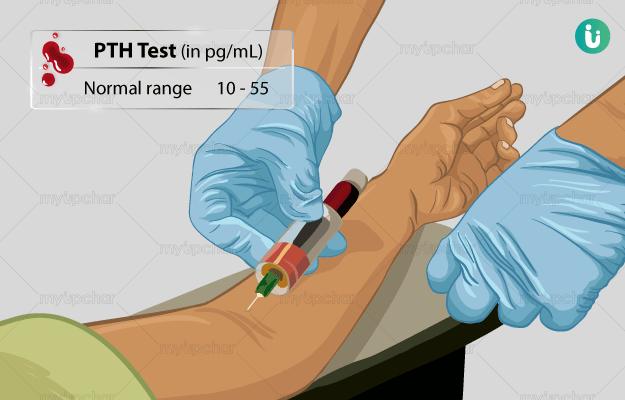
What is a Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) test?
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) is produced by four parathyroid glands in the neck. It circulates in the blood and plays an essential role in regulating calcium levels in the body. Calcium is necessary for the normal functioning of kidneys, heart, nervous system and bones.
When calcium levels reduce in body, parathyroid glands release PTH to stabilise them and n case of high calcium levels, PTH production is stopped. Thus, measuring PTH levels helps determine the cause of abnormal calcium levels in the body.
The alternate terms for this test are parathormone (PTH), intact PTH, PTH intact molecule, hypoparathyroidism - PTH blood test and hyperparathyroidism - PTH blood test.