What is a Cholesterol test/Lipid profile?
A lipid profile/cholesterol test is used to measure the amount of cholesterol in blood. Cholesterol is a waxy material that is present in all the cells of body. It is helpful in the production of various hormones, enzymes and other substances useful for digestion. Although our body produces the necessary amount of cholesterol, it can also be taken from some external sources like eggs, meat and dairy products.
Here is the complete detail about high cholesterol treatment.
Cholesterol test/lipid profile measures the amount of total cholesterol in blood along with the amount of lipoproteins that carry cholesterol, triglycerides and other fats in blood. It helps in assessing the risk of cardiovascular diseases or stroke, which can be caused by blocked or narrowed arteries due to the accumulation of cholesterol.
Different tests are available for different types of cholesterol, or a single total cholesterol test can be done for all types of cholesterol.
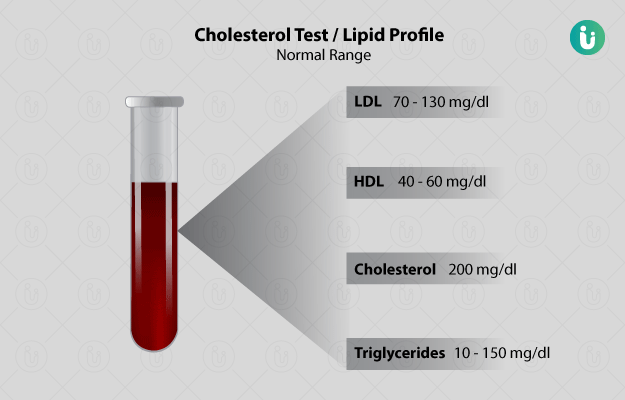
A lipid profile includes:
- Total cholesterol: Total cholesterol refers to the total amount of cholesterol present in blood including both LDL and HDL cholesterol. Cholesterol is essential for the normal functioning of body cells. It also helps in the formation of various essential substances, such as hormones and bile acids.
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL): This lipoprotein is a carrier of cholesterol in blood and is also known as “bad cholesterol” as high levels of LDL increase plaque density in arteries.
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL): This lipoprotein moves cholesterol from different parts of the body into the liver, from where it is removed from the body. It is also called good cholesterol for this reason.
- Triglycerides: Triglycerides are the main components of fat cells, generated from excess calories consumed. Fats in body are mostly stored in the form of triglyceride.
- Very low–density lipoprotein (VLDL): VLDL are responsible for carrying triglycerides in blood and is sometimes called bad cholesterol. High levels of VLDL lead to plaque build-up in arteries.
(Read More - Foods to reduce high cholesterol)