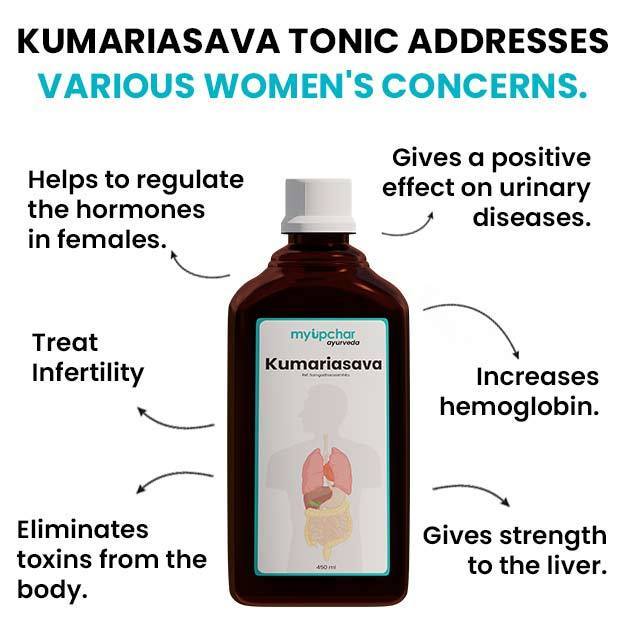
What is a CDU (Cadmium Urine) test?
Cadmium is a heavy metal that is produced as a by-product during the smelting of other metals like zinc, copper and lead. It is present in many items of daily use. For example, in mobile phone batteries, paints, plastic and fertilisers. Cigarette smoke also contains a significant amount of cadmium.
Acute or long term exposure this heavy metal may lead to toxicity that manifests in the form of flu-like symptoms at first and have grave effects on multiple organs of the body later on such as the kidneys, lungs and bones
There are several occupations which pose the risk of cadmium exposure and toxicity. These include:
- Battery manufacturing
- Smelting of metals
- Mining work
- Textile work
- Jewellery making
- Stained glass window making
- Solid waste recovery (municipality)
- Jobs requiring welding and soldering
- Manufacturing of cadmium alloys
- Manufacturing of paints and plastics which contain cadmium
A CDU test is mainly ordered to check for chronic cadmium poisoning. This is because urine cadmium levels don't rise to notable levels after an acute exposure unless it leads to kidney damage - a blood test is usually done to check for acute cadmium poisoning. A CDU test gives a more integrated estimate of the total amount of cadmium in the body and is usually done in people who have has a long term exposure to this heavy metal.
(Read more: Cadmium blood test)