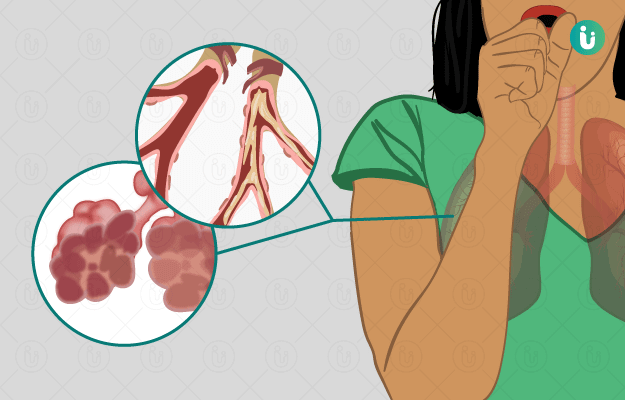
What is COPD?
COPD is a collective term for severe inflammatory lung diseases that mainly cause obstruction of the air-flow in the lungs. Worldwide, COPD is a major cause of mortality and morbidity. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 65 million people are suffering from a moderate-to-severe form of COPD globally. The prevalence of COPD reported in India is 2%-22% in males and 1.2%-19% in females.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Initially, one may not identify COPD easily as the symptoms may overlap with other respiratory conditions. The usual symptoms include:
- Difficult breathing
- Cough
- Excess mucus secretion
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Bluish discolouration of the lips or fingernails
- Fatigue
- Unusual weight loss
- Oedema in the lower extremities
COPD includes three progressive lung conditions: chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and irreversible asthma. Individuals who develop chronic bronchitis present with symptoms like persistent cough and mucus secretion. In emphysema, the alveoli (small air sacs in the lungs) are affected and get destroyed due to various gaseous irritants, for example, cigarette smoke.
If you are tired of dieting and exercising and are not able to lose weight, then use myUpchar Ayurveda Medarodh Fat Burner Capsule, it has no side effects, order it today and avail the benefits.
What are its main causes?
The most important risk factor and cause of COPD is smoking and exposure to biofuels or household smoke. Other risk factors include comorbidities such as heart disease, heartburn, depression or diabetes. Passive smoking and a rare genetic condition due to alpha-1-deficiency may have a role in COPD. Asthma can also exacerbate COPD.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
The following tests may be performed for diagnosis of COPD:
- Lung function tests: To check the lung capacity.
- Chest x-ray: To rule out other lung problems.
- Arterial blood gas analysis.
- Laboratory tests.
The Gold guidelines are usually used to make treatment choices for COPD patients. Treatments include:
- Preventive measures:
- Stop smoking and avoid exposure to smoke and other respiratory tract irritants.
- Medications:
- Bronchodilators.
- Inhaled steroids.
- Combination inhalers.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors.
- Antibiotics.
- Non-drug measures include:
- Oxygen therapy.
- Lung rehabilitation programs.
- Surgery:
- Lung volume reduction surgery.
- Lung transplant.
- Bullectomy.
It is better to prevent and stop the progression of the disease.
COPD is a persistent disease that is not curable, but with the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment, one can manage COPD to achieve a better quality of life.
(Read more: Lung infections treatment)

 COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) videos
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) videos Doctors for COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Doctors for COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)  OTC Medicines for COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
OTC Medicines for COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
 COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) articles
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) articles
 Diet for COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Diet for COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)







 Editorial Team
Editorial Team











