Most often, ovarian cysts tend to resolve in a few months without any treatment. In such cases, no symptoms may be noted.
The need for therapy or treatment will depend upon:
- The size of the cyst.
- The symptoms it produces.
- Whether the woman has had menopause.
Observing the cysts for some time
In most cases, the doctor may recommend that you do not receive any immediate treatment but keep undergoing medical tests, such as ultrasounds, to check whether the cyst is healing. Women who have reached menopause may be advised to have ultrasound scans every four months for at least a year, as they are at a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer. If the ultrasounds reveal that the cyst does not exist, no further treatment may be needed.
Medications
The healthcare provider may prescribe medications containing hormones (birth control pills) to stop ovulation. This would prevent the formation of any functional cysts.
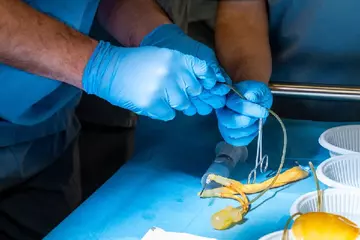
Surgery
Large-sized cysts that manifest symptoms, such as pain and inflammation or swelling, may have to be removed surgically. The surgery can be performed in two different ways:
- Laparoscopy
A laparoscopic surgery may be performed for smaller cysts that are non-cancerous. In this surgery, the doctor extracts the cyst using a device inserted through a small incision near the belly button.
- Laparotomy
Laparotomy is the surgical method used for removing the cyst that is larger in size or may be cancerous. This surgery also allows the doctor to remove the cyst and send it for further testing. If the cyst is determined to be cancerous, then an oncologist will provide further treatment. Depending on its severity, the removal of the ovary may also be necessary.
After surgery, you may experience slight discomfort in the abdominal area. However, the pain due to surgery gets better within a few days. The recovery time for laparoscopy is two weeks, while that for a laparotomy may be eight weeks.
Following the surgery, the presence of any of the following symptoms, which are indicative of an infection, must be immediately reported:
- Bleeding at the surgical site.
- Severe pain in the abdomen.
- Swelling in the operated area.
- Fever.
- Unusual vaginal discharge.
Lifestyle management
There are several helpful steps that can help immensely in dealing with ovarian cysts. These include a list of do’s and don’ts as part of health management:
- Quit smoking
There are studies that have shown that women who smoke are more prone to developing ovarian cysts. Hence, excessive smoking and intake of alcohol must be avoided at all costs.
- Limit caffeine intake
Caffeine may act as a trigger for the development of ovarian cysts. Hence, it must be consumed only in moderation.
- Limit sugar intake
The consumption of excessive sugar can lead to inflammation and swelling. Sugar and other sources of refined carbohydrates can also lead to more pain if you are already suffering from cysts. Hence, sugar intake must be restricted. The consumption of processed foods should also be avoided.
- Reduce oestrogen intake
Food sources, such as soy and food additives, contain high amounts of oestrogen and xenoestrogens. Excessive oestrogen levels in the body can lead to hormonal imbalance, which can, in turn, lead to ovarian cysts.
- Avoid steroid medications
Steroid medications can result in hormonal imbalances as well, which initiate the formation of ovarian cysts, and hence must be avoided. For pain relief, paracetamol can be used instead of regular painkillers.
- Eat a balanced diet
If you are already dealing with ovarian cysts, special care should be taken in terms of having a healthy and balanced diet. The diet must be inclusive of fruits, vegetables, and pulses to prevent the cysts from recurring. These foods are also rich in fibre, which helps in naturally healing the cysts and reducing their recurrence as well.
- Making an exercise routine
Practising yoga and other stretching exercises will not only help in healing the ovarian cysts but will also reduce the menstrual discomfort, such as period pain and cramps in the stomach and back. Regular exercises also reduce stress levels and increase blood circulation throughout the body, which in turn has a positive effect in terms of reducing ovarian cysts.
- Wear comfortable clothing during menstruation
Wearing tight and uncomfortable clothing while on your periods can put pressure on the abdomen and trigger pain. Hence, it is advisable to wear comfortable and loose clothes.
- Drink plenty of water
Consuming 7-8 glasses of water a day will help in flushing out the toxins from the body and reducing inflammation as well. Hence, it is important to keep yourself hydrated.
- Practice relaxation techniques
Stress and anxiety have a detrimental effect on health as they contribute to an imbalance of hormone levels. Stress is also a common cause of functional ovarian cysts. Hence, practising relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, exercising, or even getting a therapy, can bring the body and mind back to a balanced state.

 OTC Medicines for Ovarian Cysts
OTC Medicines for Ovarian Cysts
 Lab tests for Ovarian Cysts
Lab tests for Ovarian Cysts Ovarian Cysts articles
Ovarian Cysts articles
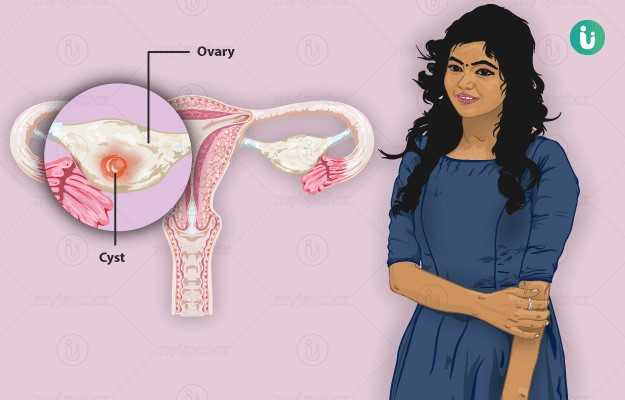
 Homeopathic Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
Homeopathic Treatment of Ovarian Cysts































 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria