What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
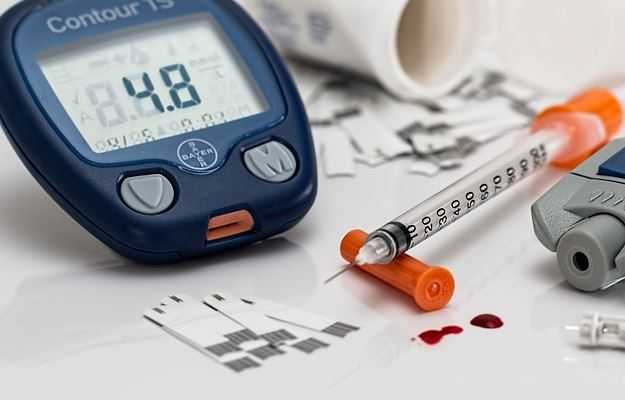
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a complication of diabetes, which occurs as a result of abnormally high levels of ketones in the blood that make it acidic. It can lead to coma or death if left untreated. It is more common in type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes rarely suffer from DKA. There is limited information on the incidence of DKA in India.
Here is the complete detail about the ayurvedic treatment of diabetes.
(Read More - Diabetic Nephropathy treatment)
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Warning signs and symptoms of DKA include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent desire to pass urine
- High blood sugar levels
- High levels of ketone in the urine
Other symptoms that may appear include:
- Constant fatigue
- Dry skin
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fruity odor on breath
- Lack of alertness or difficulty in paying attention
(Read More - Diabetic Dyslipidemia treatment)
What are its main causes?
Lack of insulin in diabetes triggers the body to use fat as a source of energy. As fat is broken down, it results in the production of ketones. These excess ketones are then excreted in the urine.
DKA is mainly triggered by:
- Infection: Presence of an illness can lead to an increase in the levels of certain hormones that nullify the action of insulin.
- Insulin regimen: Improper or missed doses of insulin can cause DKA.
- Inadequate food intake
Other factors include:
- Emotional or physical trauma
- Heart attack
- Alcohol or drug abuse, typically cocaine
- Medication use
(Read More - Ayurvedic treatment for Diabetes)
How is it diagnosed and treated?
A medical history, physical examination and laboratory tests help a doctor to diagnose the condition. HbA1c and other blood sugar measurements are done. Ketones are primarily checked if the patient is a known case of diabetes. It can be done either by a urine or blood test. Other tests include:
- Arterial blood gas measurement
- Urine analysis
- Osmolality blood test
- Biochemical tests (tests for sodium, potassium, calcium, etc.)
The goal of treatment for DKA is blood sugar control. Oral blood sugar lowering agents may be given initially, or if your sugar level is too high, insulin may be preferred. The treatment is decided based on the sugar levels of the patient. Treatment also involves fluid and electrolyte replacement.
Self-care tips:
- Carefully monitor blood sugar levels.
- After taking anti-diabetic medicines, you may feel hypoglycemic. Keeping a sugar candy or chocolate with you can be helpful in case of emergency.
- Take medicines as prescribed.
- Check for ketones every 4-6 hours when you do not feel well.
- Avoid exercising if your urine test shows presence of ketones.
- If you feel uncomfortable or any of the warning symptoms occur, call your physician right away.
Lifestyle changes:
- Restrict sugar-containing foods in the diet.
- Choose foods low in fat and high in fiber.
- Exercising is encouraged once the blood is free of ketones and sugar levels are under control.
(Read More - Diabetic Gastroparesis treatment)

 OTC Medicines for Diabetic Ketoacidosis
OTC Medicines for Diabetic Ketoacidosis