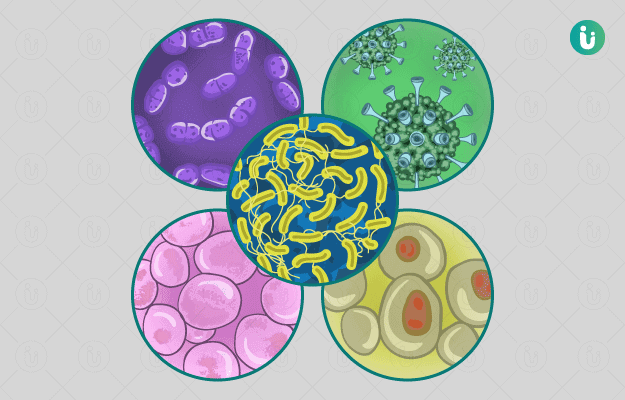
What are infections?
When disease-causing organisms invade your body, they multiply and give rise to a number of symptoms and reactions, termed as infections. Infections are caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites, which may be external or internal. Most pathogens can cause a wide spectrum of diseases. The infections can either be primary, which are a cause of current health problem, or secondary, where infection occurs because of a decreased immunity due to a prior infection or some kind of injury.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Symptoms of infection typically depend upon the site of the infection and the causative microorganism. The main symptoms are as follows:
- Swelling and redness
- Pain
- Fever
- Stomach upset
- Rashes
- Running nose
- Coughing
- Difficulty in movement
- Memory loss
What are the main causes?
The causative organisms are bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites, such as ringworm, roundworm, lice, fleas and ticks. The infections are transmitted in many ways as discussed below:
- Person to person.
- Animal to person.
- Mother to unborn child.
- Contaminated food and water.
- Insect bite.
- Using inanimate objects touched by an infected person.
- Iatrogenic transmission (due to infected medical devices).
- Nosocomial infection (hospital acquired).
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Diagnostic tests follow your medical history taken by the doctor. Following are the commonly advised diagnostic tests:
- Physical examination.
- Microbiological testing.
- Laboratory tests, such as testing the samples of blood, urine, stool, throat swabs and cerebrospinal fluid.
- Imaging studies, such as X-ray and MRI.
- Biopsy.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) based test.
- Immunoassays: ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) or RIA (Radio Immuno Assay).
Once the causative organism of your infection is known, treatment becomes easier. Following treatment is available for infections:
- Medications:
- Antibiotics.
- Antiviral drugs.
- Antiprotozoal drugs.
- Antifungals.
- Vaccination.
- Alternative medicine:
Natural remedies like green tea, cranberry juice, ginger and garlic have been claimed to fight against infections.
Although natural remedies and alternative treatment, especially Ayurvedic formulations to treat infections are available, it is better to seek doctor’s advice if you notice symptoms of any infection. Judicious use and completing the regimens of antibiotics is important to avoid resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics. All infections need not be treated, as some are self-limiting. But severe infections require medical advice and timely treatment. Maintaining cleanliness, hygiene and proper sanitation can avoid the transmission of infections, thereby limiting the spread of infectious diseases.

 Doctors for Infections
Doctors for Infections  OTC Medicines for Infections
OTC Medicines for Infections
 Infections articles
Infections articles






 Dr. Anurag Shahi (AIIMS)
Dr. Anurag Shahi (AIIMS)
 Editorial Team
Editorial Team











