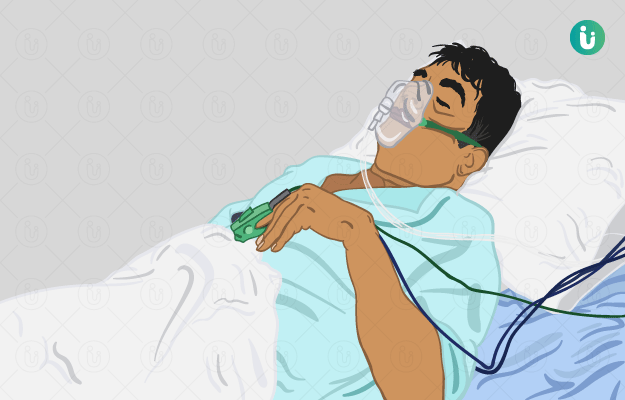
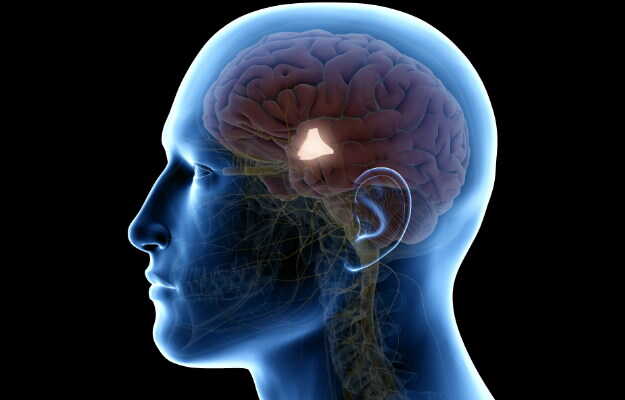
A coma is a state of deep unconsciousness in which a person is unresponsive to their environment. It is most often caused by injuries to the brain and/or the central nervous system or due to a few underlying illnesses. Depending on the cause, it can occur rapidly or over a period of time and typically lasts for a few days to weeks.
If a person enters into a coma, it is usually a medical emergency and the patient requires immediate medical attention to preserve their life and brain function. Investigations include physical examination, blood tests and brain scans.
Many people are able to recover from it, however, some people end up with major or minor disabilities. The risk of death cannot be denied in the case of a coma.

 Doctors for Coma
Doctors for Coma  OTC Medicines for Coma
OTC Medicines for Coma