What is H. pylori?
H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori) is a bacterium that enters our body and harbours in the stomach. It often acts as a commensal (remains in the stomach and does not cause any trouble); but in few people, on encountering suitable conditions, it grows and causes ulcers in the stomach. It usually results in a chronic condition called GERD (gastro-oesophagal reflux disease) that can be easily treated with antibiotics.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
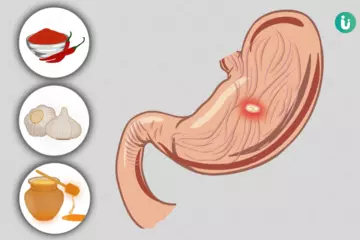
When H. pylori enters the stomach, it causes increased acid production in the stomach and also damages the inner lining of the stomach resulting in an ulcer (sometimes it can cause multiple gastric ulcers). Symptoms of the ulcer include:
- Pain in the upper abdomen (Read more: Stomach pain causes)
- Abdominal pain, increasing on eating and settling in a couple of hours after meals; also increasing on prolonged fasting or eating late meals
- Nausea
- Vomiting (sometimes blood is present in vomitus)
- Abdominal bloating
- Burping
- Weight loss and anaemia
- Black coloured stool
What is its main cause?
How H. pylori enters the body is unknown but on entering the body it causes ulceration of the stomach lining. H. pylori itself is the cause of gastric ulceration but there are certain risk factors, which can predispose a person to be infected by the bacteria.
These risk factors include:
- Remaining in contact with a person who is already infected with H. pylori
- Poor water quality (drinking such water can cause this infection)
- Living in high-density areas
- Living with poor personal hygienic conditions
How is it diagnosed and treated?
An adequate medical history with a thorough clinical examination can lead to the diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD). To diagnose H. pylori infection certain investigations are a must. These investigations include:
- Blood tests like CBC along with a stool test
- Breath urea test,
- Upper digestive tract endoscopy
Usually H. pylori infection is treated with oral medication, which includes a combination therapy of following class of drugs:
- Antibiotics – Drugs like amoxicillin, metronidazole, tinidazole, clarithromycin etc. help in eliminating the bacteria
- Proton pump inhibitors and histamine blockers – these drugs help in reducing the acid content of the stomach and help in the healing of the ulcer
- Bismuth subsalicyclate – It protects internal lining by providing a coat over the ulcer

 OTC Medicines for H. Pylori
OTC Medicines for H. Pylori