What is blood thinning?
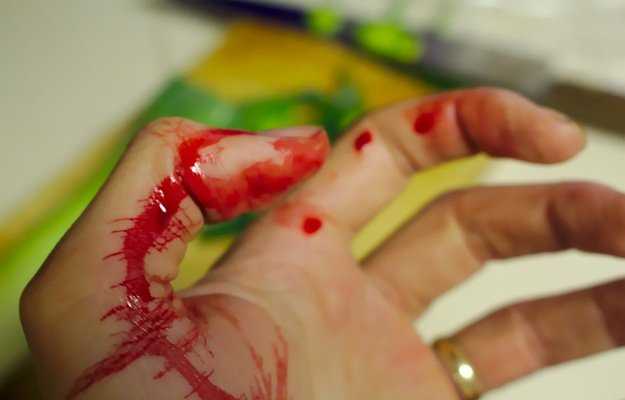
Blood thinning is a condition in which the blood is unable to clot, leading to bleeding disorders. Improper or inadequate clotting can be due to a defect in the blood components or clotting factors. Thirteen clotting factors are produced by the body, and any deficiency or defect in any of the clotting factors causes blood thinning and, thereby, bleeding disorders.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The following symptoms are observed in individuals with bleeding disorders:
- Unexplained nosebleeds.
- Bleeding gums
- Bleeding for extended periods after minor cuts and injections.
- Excessive bleeding during and after surgery.
- Bleeding for a long period after dental procedure.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding without any clots in the blood.
What are the main causes?
The bleeding disorders occur due to missing or damaged clotting factors, reduced platelet count in the blood, or improper functioning of the platelets. The blood-thinning disorders can be classified on the basis of their underlying cause:
- Genetic or acquired causes like haemophilia (an inherited bleeding disorder).
- Due to some other health conditions like anaemia, deficiency of vitamin K, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, liver cirrhosis, and leukaemia.
- Prolonged intake of some medications like aspirin, warfarin and heparin.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
The diagnosis of a blood thinning disorder is made in the following manner:
- A review of complete medical history.
- Physical examination.
- Blood test to determine a complete blood count.
- Tests to identify the clotting time of the blood.
- Tests to detect any blood protein deficiency.
The exact treatment varies with the condition that causes blood thinning and its the severity of the condition. In some bleeding disorders, clotting factors are given as infusions to prevent or treat blood thinning, whereas, in other disorders, topical products and nasal sprays are used. The following treatment options may be prescribed by the doctor to treat bleeding disorders:
- Vitamin K injection.
- Blood plasma or platelet transfusion.
- Medications that help in blood clotting.
- Other medications like hydroxyurea to cure anomalies related to the platelets.

 OTC Medicines for Blood Thinning
OTC Medicines for Blood Thinning