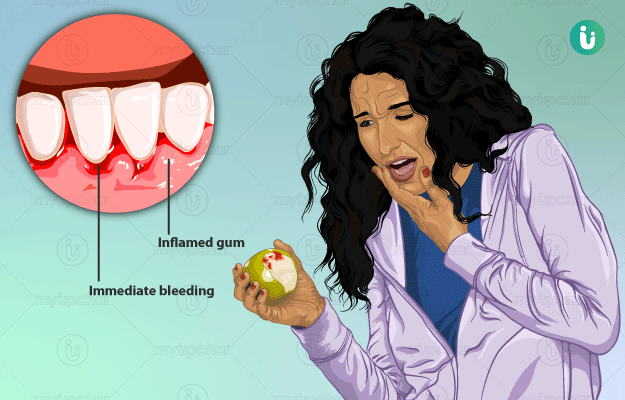
What are bleeding gums?
Bleeding gums are a sign of unhealthy or diseased gums. Treating the cause, maintaining proper dental hygiene and a healthy lifestyle are important factors in the management of bleeding gums.
What are its main associated signs and symptoms?
Before the gums start bleeding, they are inflamed (red and swollen) and bleed easily on brushing or flossing the teeth (gingivitis). Bleeding increases when the inflammation becomes severe and extends to the jaw bone (periodontitis). As the disease progresses, various symptoms are seen:
- Bad breath
- Pain and difficulty while chewing food
- Teeth getting exposed, with pulling away of gums
- Loosening of teeth, with an increase in sensitivity of teeth
- Accumulation of pus in the gums
- Metallic taste in the mouth, increased secretion of saliva and fever occur when infection is very severe
What are the main causes of bleeding gums?
Different causes that lead to bleeding gums include:
- Incorrect method of brushing teeth and flossing or using a hard brush
- Lack of dental hygiene
- Infection due to formation of plaque at the junction of gums and teeth
- Changes in hormones during pregnancy
- Deficiency of vitamin C and vitamin K
- Bleeding disorders
- Blood-thinning medicines
- Blood cancer such as leukaemia
- Improper dentures
- Diabetes
- Cigarette smoking
- Immunocompromised conditions like AIDS
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Dentists diagnose bleeding gums based on examination of teeth along with symptoms and history of other diseases (such as diabetes). Various investigations that help in the diagnosis include:
- Blood tests
- Complete blood count helps in detecting infection in the body
- According to research studies, high cholesterol levels and increased C-reactive protein is also noted with gum and teeth diseases
- X-ray: Jawbone X-ray helps in detecting the extent of gum disease to the jawbone
Treatment of bleeding gums is aimed at stopping the progression of disease and preventing further damage to teeth and gums.
- Proper brushing and flossing practices help in reducing plaque.
- Antibiotics help in getting rid of infection.
- Hot water or hydrogen peroxide for rinsing mouth helps in decreasing plaque.
- Dentists remove the layer of plaque from the surface of the teeth by a procedure called scaling.
- Vitamin supplements are used for treating bleeding gums due to deficiency of vitamin C or K.
- Avoid smoking and tobacco use completely.
- Avoid blood-thinning medicines like aspirin unless recommended by your doctor.
- Regular dental check-ups and professional teeth cleaning help in maintaining dental hygiene.

 Doctors for Bleeding Gums
Doctors for Bleeding Gums  OTC Medicines for Bleeding Gums
OTC Medicines for Bleeding Gums
 Bleeding Gums articles
Bleeding Gums articles
 Home Remedies for Bleeding Gums
Home Remedies for Bleeding Gums







 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla