What is rheumatic heart disease?
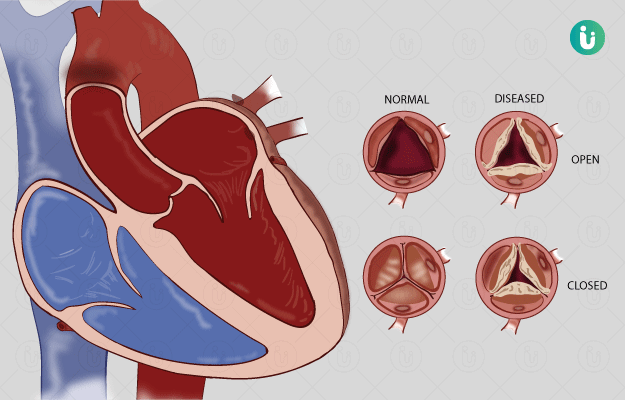
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is a disorder of the heart in which irreversible valve damage and heart failure, along with, organ damage is seen following a streptococcal throat infection. Acute rheumatic fever (ARF) is the precursor of this disease.
Here is the complete detail about heart disease treatment.
(Read More - Coronary Artery Disease)
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Sometimes RHD can occur without any symptoms and symptoms, if present, may include:
- When damaged heart valves are infected, fever is an associated symptom.
- Swelling (oedema).
- Problems with breathing in lying down position (orthopnoea) and/or breathlessness on exertion.
- Pain in the chest or heart palpitations.
- Arousal from sleep feeling the need to sit or stand up (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea).
- Fainting (syncope).
- Heart murmur.
- Stroke.
(Read More - Rheumatic Heart Disease)
What are the main causes?
The main cause of RHD is group A streptococci infection, which causes an abnormal autoimmune response in a host who is genetically susceptible. This exaggerated reaction leads to inflammation across multiple tissues in the body.
(Read More - Heart Failure treatment)
How is it diagnosed and treated?
The physician will take a detailed history of the symptoms and medical history (evidence of past ARF or streptococcal infection) along with a thorough physical examination. Sometimes, a heart murmur is encountered during this examination, which may suggest RHD. However, in some patients with RHD, a heart murmur may not be heard. The physician might also suggest the following tests:
- Chest X-ray – For checking heart enlargement or presence of fluid in the lungs.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – For checking heart chambers enlargement or abnormality in the heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
- Echocardiogram – For checking the heart valves (for damage, infection).
Management of RHD varies as per the severity of the disease and includes:
- In cases of heart failure, hospital admission is necessary for treatment.
- For infections, generally seen in the heart valves, antibiotics (mainly penicillin) are also prescribed.
- For prevention of stroke or when thinning blood is required for replacement of valves, blood-thinning medicines are prescribed.
- To open up stuck valves, balloon surgery is required where a balloon is inserted through a vein.
- For repairing or replacing damaged heart valves, heart valve surgery may be required.
(Read More - Endocarditis treatment)

 OTC Medicines for Rheumatic Heart Disease
OTC Medicines for Rheumatic Heart Disease