Having thin or watery semen does not necessarily mean that you have a medical problem. Simple measures like a minor modification to your diet or inclusion of dietary supplements or taking the pace of your sexual activity could help. In the event that the semen is thin due to lowered sperm count, it is important to remember that you are not entirely infertile. It may take a bit longer to be able to impregnate, but it certainly does not eliminate your chances at conception. Looking for some form of therapy or treatment for this condition can help improve these changes. An altered lifestyle which includes less alcohol and smoking, more exercise and a balanced diet can also help improve the overall health of semen significantly. Here is precisely what all you can do to deal with thin, watery semen:
Consume a balanced diet
Certain nutritional deficiencies are responsible for a lowered sperm count, which makes your semen look thin and watery. Consuming a balanced diet with the right composition of these nutritional components will ensure the absence of these deficiencies.
Increase the intake of zinc in your diet
While balanced diet, per se, is determinant of your sperm and seminal health, there are certain dietary components, which are crucial to the synthesis of sperm, zinc being one of the most important of these. Its deficiency may cause your sperm to become thin and watery and worsen your concerns. In order to prevent this, it is important that you include sufficient amount of zinc in your diet, which can be achieved by the intake of animal products like dairy, meat, fish and eggs along with legumes and nuts.
Consider taking supplements
At times when you are unable to keep up with a healthy diet, it is important that you consult a doctor and talk about the intake of nutritional supplements. Getting yourself tested for any nutritional deficiencies, must probably form the first measure to be taken in case you doubt that the consistency of your semen is becoming thin. In some cases with zinc deficiency, supplements may be prescribed and must be taken on time.
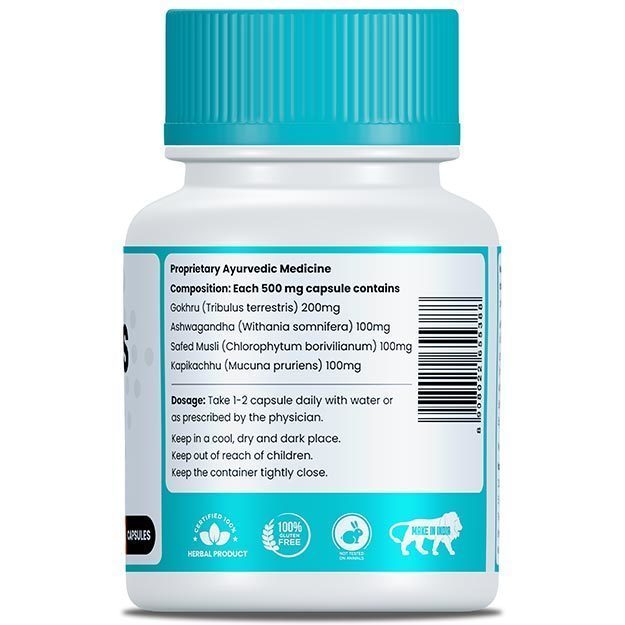
Take herbal supplements
Certain herbs have been recognised to improve sperm count and quality. The inclusion of these herbs can help in improving the thickness and viscosity of the semen. Best of these herbs include ashwagandha, maca, fenugreek, Catuaba bark and cordyceps. Simple kitchen ingredients like ginger supplements can also help with your concern. However, for the precise dosage and use, it is important that you talk to your Ayurvedic doctor.
Modulate your sexual activity
Unlike women, men need some time before they can recover and have sex again after they ejaculate. Having sex too often or even masturbating each day may eventually make your semen thin and watery because the sperms are not getting enough time to regenerate and again. In such cases, the limitation of sexual activity can be helpful. Since different men require different time to regenerate, which can vary from a few hours to a few days, it is important that you understand your body and limit sexual activity before you are completely ready. At the same time, it is important that you do not abstain from sexual activity completely, as this can also reduce your sperm count and viscosity of the semen.
Talk to your doctor
If you often notice that your semen is getting thinner and more watery, it is important that you do not ignore this and visit a doctor to determine the exact cause, which will be managed accordingly. Moreover, certain drugs like alpha blockers can aggravate your problem of a watery semen. Your doctor may also modulate the dosage of these drugs. On the other hand, if you suffer from anejaculation, that is, have no semen at all during sexual activity, it is all the more important to see a doctor since this often relates with serious underlying causes like structural and functional changes at the bladder neck.
Manage stress
Certain studies have also found that a low sperm count or the absence of ejaculate in men could also be due to psychogenic causes. So, it is important that you do not worry too much about your sperm count or semen and focus on the pleasure of the act. This will most likely help with your concern. Other than this, measures to reduce stress and anxiety, like meditation and yoga may prove to be helpful.
Opt for therapy
In some men, stress, anxiety and relationship problems along with performance pressure can alter the quality and quantity of semen secreted. In such men, counselling, therapy and couples’ therapy can be helpful. Further, couples’ therapy may help to improve communication between the partners, which will make it easier to deal with the problem.
Lifestyle changes
A healthy diet and exercise regimen will go a long way in improving the quality and viscosity of semen. While you are exercising, it is important to protect your man parts as repeated trauma and injury can affect the quality of your semen. Stay away from contact sports and activities that can aggravate this injury. Another thing which you can do for your health and that of your semen is stop smoking. Not only does smoking negatively affect the quality of your semen but also can lead to infertility in the long run.