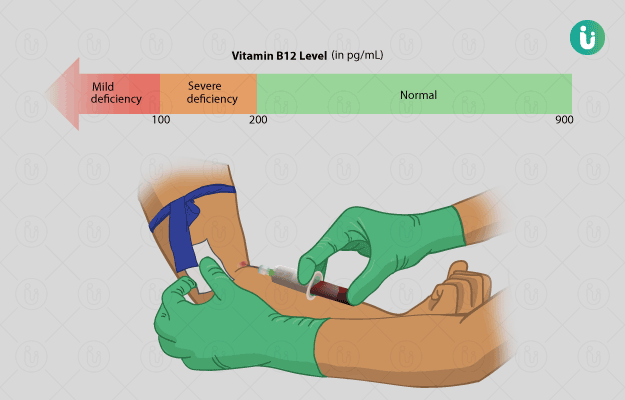
What is a Vitamin B12 test?
Vitamin B12 test is a blood test that is done to detect serum vitamin B12 levels. Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin necessary for vital neurological functions and synthesis of DNA and blood. This vitamin is absorbed in terminal ileum (a part of small intestine) in the body, and a glycoprotein intrinsic factor is necessary for the absorption Excess amounts of B12 vitamin is stored in liver Evaluation of vitamin B12 in the serum is advised most commonly in conditions, such as anaemia and muscle weakness. However, these results may not be sufficient. Vitamin B12 in the serum is bound to the protein transcobalamin (TC). Nearly, 80% of the vitamin present on TC I is inactive, while the remaining 20% is actively transported by TC II. Often, low serum cobalamin levels are due to a deficiency of TC I.
Although low serum levels of B12 indicate a deficiency of the vitamin and higher concentrations indicate normal levels, the interpretation of intermediate concentrations is unclear.