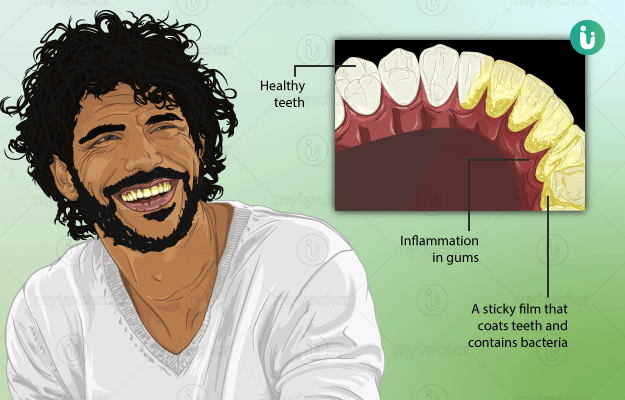
What is dental plaque?
Dental plaque refers to the deposition of a soft and sticky substance around and between the teeth. It is one of the most common causes of tooth decay and gum diseases. Since this substance is white in colour, it may be hard to detect at first. However, once it begins to get stained and yellowish, it becomes visible and spoils the appearance of your smile.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Plaque is a sticky white substance which is not very easily visible. However, it can be seen with the naked eye when one has not recently brushed the teeth. It may be visible early in the morning after a relatively longer duration of not brushing the teeth. On scraping the tooth near the gum line, white paste-like material comes off.
What are the main causes?
Plaque is formed when there is a breakdown of sugar/sucrose/carbohydrates in the mouth by the bacteria and they start depositing and sticking to the teeth.
It begins to form when carbohydrate-rich foods are not cleaned properly from the mouth. The residual sugars in the mouth allow for bacterial growth. As the breakdown of carbohydrates proceeds, acids are formed as by-products, which can cause long-term damage to the tooth enamel.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Dental plaque can be seen easily at home. Hence its diagnosis is very easy. One can perform a simple test at home in order to stain the plaque and detect the places at which it has been deposited. To do this, one can purchase the red disclosing tablets present in most grocery stores and pharmacies. Chewing one of these helps in staining the plaque and making it visible.
The dentist may also use this test to diagnose plaque.
Dental plaque can be removed at home easily. It can be done by first flossing the teeth and then brushing them to get rid of the plaque. When the amount of plaque deposition is less, simple brushing also helps in getting rid of it.
Preventive measures include:
- Cleaning your teeth twice a day.
- Using a fluoride-based toothpaste.
- Using anti-bacterial mouthwashes.
- Flossing between the teeth to remove leftover food particles.
- Getting regular dental check-ups done.
- Reducing the amount of sugar in one’s diet.

 OTC Medicines for Dental Plaque
OTC Medicines for Dental Plaque
 Dental Plaque articles
Dental Plaque articles



 Editorial Team
Editorial Team