What is cervical dystonia?
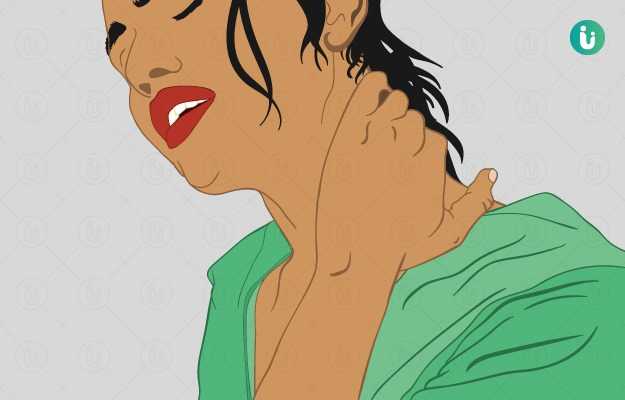
Cervical dystonia (CD) is a rare neurological disorder also known as spasmodic torticollis and is a type of focal dystonia. It is marked by an abnormal and involuntary contraction of neck muscles. It may cause your head to tilt to the side, back, or forward, and your shoulder may also contort up. Although CD can occur in men and women of all ages, it is more commonly reported in women and the population aged 40 to 50 years. CD can be of two types, primary or isolated and secondary.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The most common sign of CD is the abnormal involuntary contraction of the neck muscles. The muscle spasms can be sustained, jerky or a combination of both and can cause discomfort, stiffness, and pain. This contraction may extend and spread to the shoulder muscles, but is unlikely to affect the muscles beyond shoulders.
The sustained contraction causes an awkward posture of the neck and head, whereas the periodic contraction causes jerky head movements. The most common awkward posture observed is the rotation of head towards the sides as the chin twists towards the shoulder.
What are its main causes?
Mostly, the underlying cause of isolated CD is unknown, and only the neurological factors seem to be responsible for its occurrence. The causes of primary CD are:
- A family history of CD
- Multiple gene mutations/genetic causes
- Environmental factors
The causes of secondary CD are:
- Use of antipsychotic drugs
- Use of drugs to treat nausea that block the dopamine receptors
- Toxins
- Presence of other neurodegenerative diseases
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Most laboratory tests such as imaging techniques are normal in those with CD; therefore, a clinical examination is done to diagnose the disorder. The following measures are useful in the diagnosis of CD:
- Clinical examination and knowledge of CD
- Detailed medical history of the individual
- Magnetic resonance imaging may help if the spinal cord compression is suspected
- Electromyography may help if there is any sign of nerve irritation
The effectiveness of the treatment method of CD may vary from person to person, and most of the methods are to relieve the symptoms. The treatment options available for CD are:
- Botulinum toxin injections
- Oral medications
- Surgery
- Physical therapy
Although stress has no connection with CD, it may worsen the symptoms. The dystonia may be activated and symptoms worsened due to stress, excitement, or certain postures.
Minimising stress and managing your postures can help you manage the symptoms. Using head and neck braces can also help you reduce the pain and discomfort.

 Doctors for Cervical Dystonia
Doctors for Cervical Dystonia  OTC Medicines for Cervical Dystonia
OTC Medicines for Cervical Dystonia