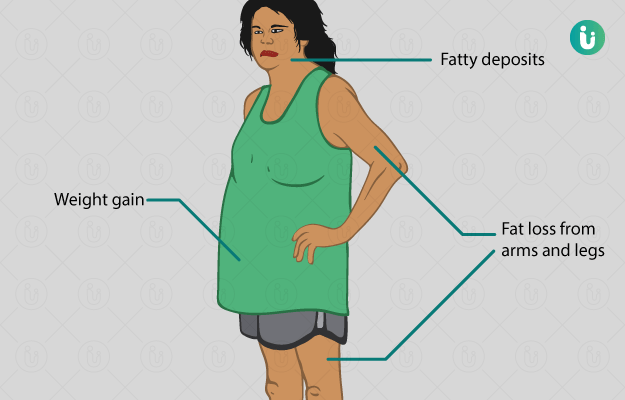
What is Cushing’s syndrome?
Cushing’s syndrome is a hormonal disorder, which occurs due to the imbalance of the hormone cortisol (higher than normal cortisol levels) in the body. Cortisol is termed as the “stress hormone” as its levels increase during periods of stress. It can be endogenous (caused by internal factors) or exogenous (caused by external factors). Variable estimates show that 40 to 70 individuals per million are affected by Cushing’s syndrome worldwide. Its incidence in India varies from 0.7 to 2.4 per million population annually as per several population studies.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Clinical features may be variable and include the following:
- Obesity, mostly seen in the upper body
- Moon face
- Buffalo hump on the back
- Irregular menstruation
- Reduced sex drive
- Depression
- Psychosis (a severe mental disorder)
- Cognitive disorders
- Weak muscles
- Bone fractures
- Improper growth in children
In adults, Cushing’s syndrome usually occurs between the ages of 30 to 50 years but can also develop in children. The incidence of Cushing’s syndrome is much higher in women than men (3:1 female to male ratio). Some uncommonly seen features are:
Other diseases (differential diagnosis) that can have similar symptoms include:
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOD).
- Metabolic syndrome (a collection of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease).
What are its main causes?
The main cause that results in the development of this syndrome is the frequent use of high-dose cortisol, especially glucocorticoids. Cortisol is useful as it has the following functions:
- Maintains blood pressure and blood glucose levels
- Reduces inflammatory conditions
- Converts food into usable energy within the body
However, an imbalance can result in abnormal levels of cortisol which can lead to complications in the long run. It can be endogenous or exogenous (use of oral corticosteroids for a long period).
Other causes include:
- Pituitary gland tumours
- Ectopic tumours that generate the hormone ACTH
- Adrenal gland tumours
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis may mainly include:
- Medical history.
- Physical exam.
- Lab tests.
Glucocorticoids are used mainly for anti-inflammatory, autoimmune, and neoplastic (tumour) diseases. Therefore, proper medication history of the patient is usually required. Other diagnostic tests that may be performed are:
- A 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC).
- Late night-salivary cortisol.
- Low-dose dexamethasone suppression test (LDDST).
- Overnight dexamethasone suppression test (ONDST).
- CT scan of the adrenal glands.
Tests to diagnose an underlying condition that may be the cause of Cushing syndrome include:
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone test (CRH).
- High-dose dexamethasone suppression test (HDDST).
- Bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling (BIPSS).
Treatment plan for Cushing’s syndrome includes:
- Medical therapy: Depending on the underlying cause of this syndrome medications are given as follows.
- To inhibit steroid production.
- Glucocorticoid receptor inhibitors.
- Modulate ACTH release.
- Adrenolytic drugs.
- If you have been taking cortisol, a lower dose is prescribed to reduce the symptoms.
- Surgery:
- Tumour surgery or removal of adrenal glands may be indicated.
- Pituitary radiotherapy.
Self-care tips:
- Follow the medication regimen prescribed by the physician.
- Avoid smoking and consumption of alcohol, as they can cause more harm and may lead to complications.
- Follow a well-balanced diet or consult a dietician.
- Do regular low-intensity exercises, as there may be a risk of fractures while performing high-impact exercises or sports.
- Avoid stress so that hyperproduction of cortisol is reduced.
Cushing’s syndrome can be managed if the above measures are followed judiciously and the physician is consulted as necessary.

 Doctors for Cushing's Syndrome
Doctors for Cushing's Syndrome  OTC Medicines for Cushing's Syndrome
OTC Medicines for Cushing's Syndrome