Hydroceles usually do not require treatment unless causing distressing symptoms.
In babies, the hydrocele usually disappears on its own within a year after birth, as the fluid around the testis is absorbed via the surrounding veins.
For hydroceles that are caused due to testicular pathologies, the pathology is to be addressed and treated.
The medical management (non-surgical) of hydroceles involves injecting a sclerosing agent (special chemical) which dries up the fluid in the sac. This procedure is used in smaller, uncomplicated hydroceles where the patient is not willing to opt for surgery. However, there is a chance of recurrence in this method.
Another method involves drainage of the fluid present in the sac via needle aspiration (sucking the fluid through a wide-bore needle). This procedure is associated with an increased risk of infection.
Surgical management is the preferred mode of treatment. The procedure is called hydrocelectomy. It is a day-care procedure and is quite risk-free with a good outcome. The technique of the procedure varies according to whether the patient is a baby or an adult. Aftercare is important to prevent complications.
In hydroceles caused due to testicular tumours, the affected testis is removed.
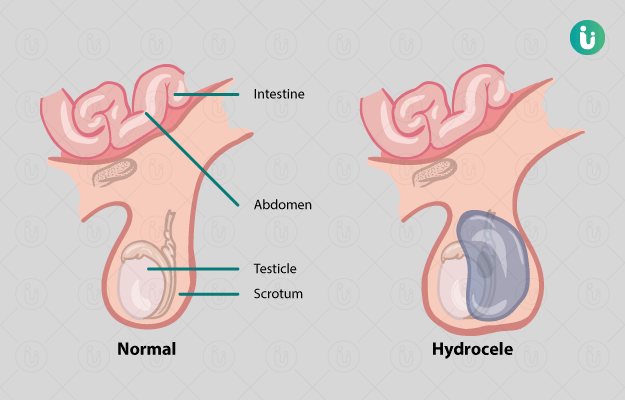
If the hydrocele is associated with a hernia, a hernia repair is also done along with surgically strengthening the muscles of the abdominal wall.
Post-surgery aftercare is important to prevent any complications, mainly infection.
(Read more: Homeopathic treatment for Hernia)

 Doctors for Hydrocele
Doctors for Hydrocele  OTC Medicines for Hydrocele
OTC Medicines for Hydrocele
 Hydrocele articles
Hydrocele articles
 Homeopathic Treatment of Hydrocele
Homeopathic Treatment of Hydrocele




































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team

 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria