Surgery
Surgery is the choice of treatment for hernias. It involves pushing back the contents of a hernia into the abdomen or removing it entirely and closing the gap with stitches. A mesh (synthetic or animal-derived) is used to support the weak tissues and muscles, which might have let the contents protrude through it.
Surgery can be performed in two ways: open or conventional surgery and minimally invasive or laparoscopic surgery. In an open surgery, a long and large cut is made at the site of a hernia and the weak muscles are repaired. In a laparoscopic or keyhole surgery, multiple small holes or cuts are made, and the surgery is performed using fine tube-like instruments. There is a camera fitted to help the surgeon get a detailed view on a monitor and to perform the necessary procedure.
In inguinal hernias, herniotomy, herniorrhaphy, or hernioplasty are the key procedures performed. Other variations of surgeries for inguinal hernias, such as Kuntz operation, Andrew’s imbrications, or Mcvay or Nyhus repair, can be performed, depending on the type of repair needed and will be decided by the surgeon. Many types of surgeries are done to manage different hernias.
Surgery is not always the only treatment option for hernias and may not be necessary if your hernia, irrespective of its type, is not causing any major health issues. Moreover, surgery is avoided in old people and in those who are seriously ill.
Medications
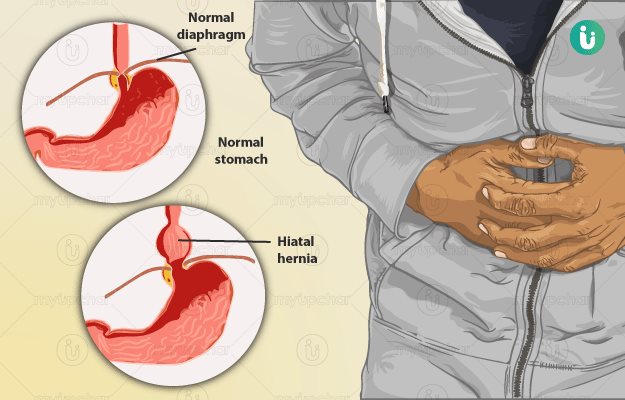
Occasionally, during a hiatal hernia, over-the-counter and other medications may be prescribed that help reduce stomach acid, thus relieving the discomfort and other symptoms that you might be experiencing. Some of these medicines are painkillers, H-2 receptor blockers that act against histamine, antacids and proton pump inhibitors (drugs that reduce the production of stomach acid).
Lifestyle management
Changes in the diet can often treat the symptoms of a hiatal hernia but will not cure it completely. A heavy meal in terms of the quality as well as the portion size should be avoided. A person should avoid lying down or perform strenuous physical activity after a meal. Hiatal hernia patients can reduce the acid reflux problem by avoiding spicy or sour foods that trigger the acid reflux. Also, avoid smoking until the symptoms persist. Body weight should be kept in check and measures should be taken to keep it in the normal range as per the person's height.
Some exercises may help strengthen the muscles around the hernia site, which may reduce some of the symptoms. However, over performing the exercises or doing it without the guidance of a qualified practitioner can increase the symptoms and even worsen the condition. Therefore, it is better to consult a physiotherapist and perform exercises under supervision.
If after undertaking all the necessary measures, the symptoms are not relieved then a surgery may be done to correct a hernia.

 Doctors for Hernia
Doctors for Hernia  OTC Medicines for Hernia
OTC Medicines for Hernia
 Hernia articles
Hernia articles
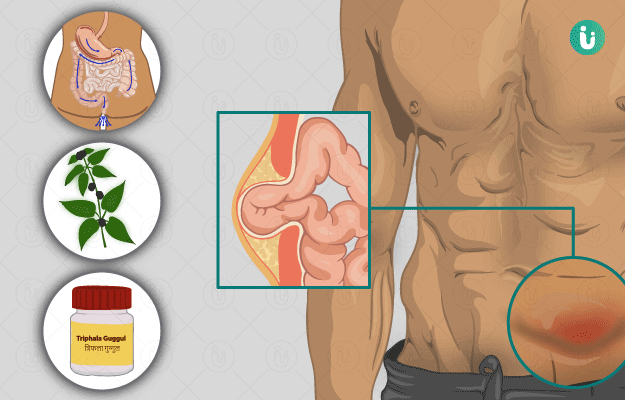
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Hernia
Ayurvedic Treatment of Hernia
 Diet for Hernia
Diet for Hernia
 Homeopathic Treatment of Hernia
Homeopathic Treatment of Hernia
 Yoga for Hernia
Yoga for Hernia




































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team


 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria