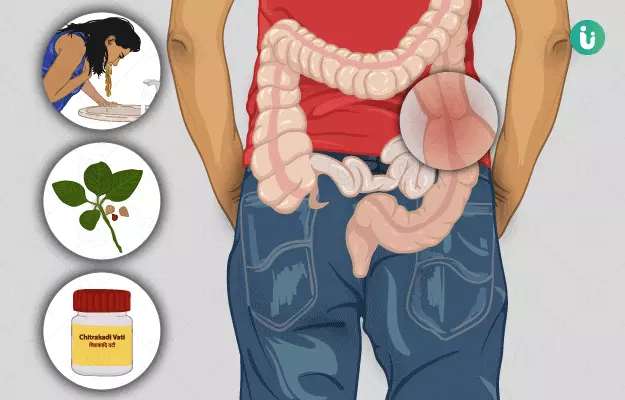
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a condition that affects the intestinal motility and manifests in the form of diarrhoea and constipation. Those with IBS are typically unable to digest their food well, which leads to frequent passing of formed or loose stools with a foul odour.
In Ayurveda, IBS is denoted as grahiniroga. The term grahani came into existence from the word grahana (holding) which refers to the holding up of food and avoiding its downward movement for the digestion process to be completed at all stages. In case of an imbalance or derangement of grahini, undigested food keeps on being released for expulsion in short-intervals, leading to symptoms such as diarrhoea, constipation and stomach pain. People with IBS also experience depression, flatulence, aversion to sexual intercourse, mouth and throat dryness, ringing in the ears and other common symptoms. Certain food substances, fluctuations in hormone levels, stress or other health conditions can be triggers for grahaniroga.
Ayurvedic herbs like shunthi (dried ginger) and chitraka (leadwort) are used to treat grahani. Ayurvedic formulations of shankha vati, jatiphaladi churna and panchamruta parpati are helpful in treating grahani. Therapies such as virechana (purgation) are effective in treating diarrhoea and dysentery in people with IBS. People diagnosed with IBS should consume wholesome, fresh and organic foods. They should eat foods at specific time intervals, in proper quantities and try to avoid stress.