According to the World Health Organization (WHO), tobacco kills around eight million people each year. It is a well-established fact that the consumption of tobacco in any form, smokeless or smoked, can create irreversible damage to the body—the most deadly being cancer.
However, before reaching that stage where the body develops cancer, it gives us many signs and symptoms which should not be ignored. For example, our oral cavity presents with precancerous lesions. If diagnosed early, these precancerous lesions can be completely reversed—taken back to normal in no time. One of the most common precancerous lesions seen in tobacco consumers is leukoplakia.
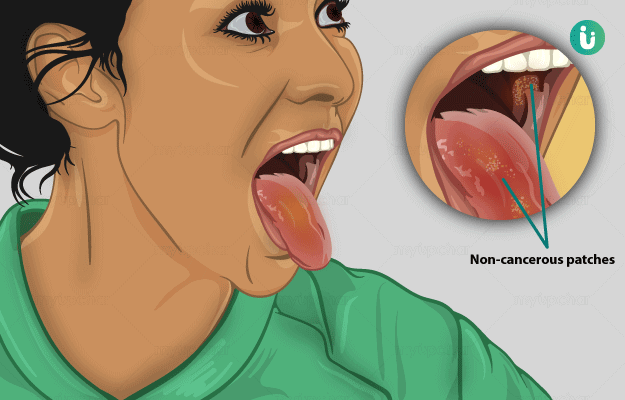
Leukoplakia is a white patch or plaque that is not associated clinically or pathologically with any underlying disease. It is not caused by any physical or chemical agents, but only due to the continuous use of tobacco. It is usually seen in men during adulthood. The lesion of leukoplakia is usually white in colour and does not scrape off on rubbing. It is painless and can be present anywhere in the oral cavity (mouth).
Though the main reason for leukoplakia is the use of tobacco, the risk factors include oral candidiasis (a fungal infection), radiation therapy, alcohol consumption and ill-fitted dentures (read more: artificial teeth). If the person visits their dental surgeon early enough, this lesion can be treated and reversed completely. If the person does not pay attention to the lesion in the primary stages, the lesion may become firm, speckled and would start bleeding, which is a sign of cancer.
Read more: White-coated tongue
After the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe vitamin A and beta carotene supplements to reduce the size of your lesion. The more aggressive lesions and the suspected cancerous lesions would require surgical treatment.
Read on to know more about leukoplakia.

 Doctors for Leukoplakia
Doctors for Leukoplakia