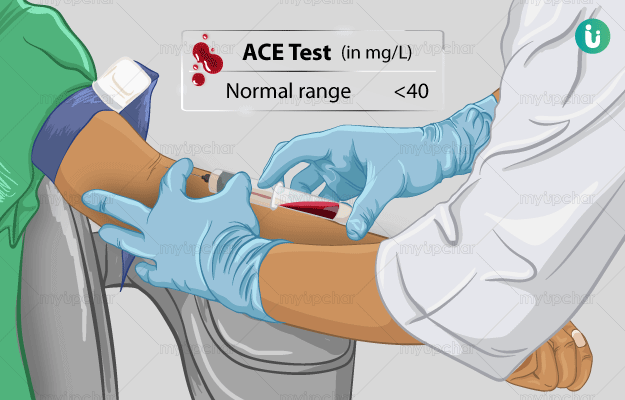
What is Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) test?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) plays an important role in the regulation of blood pressure. ACE levels are usually high in sarcoidosis patients. Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease marked by the formation of granulomas under the skin. These granulomas appear as small tiny bumps, along with other symptoms such as watering of the eyes and persistent coughing.
An ACE test is done to measure the level of Angiotensin-converting enzyme in the bloodstream. This test mainly helps check for the presence of sarcoidosis in patients; however, abnormal ACE may also be an indication of other diseases like diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism.