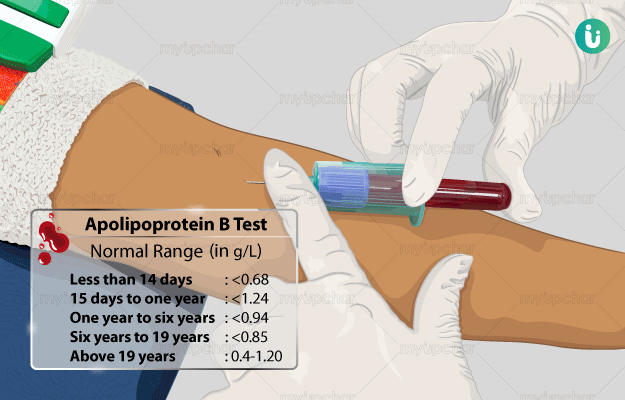
What is an Apolipoprotein B test?
The apolipoprotein B test is a blood test that helps to check the levels of a polypeptide - apolipoprotein B in your body. It is sometimes also referred to as apo B or apolipoprotein B-100 test.
Lipoproteins are complex molecules composed of lipids and proteins. The protein motifs help the insoluble fats to travel easily through blood. They also help in fat metabolism.
Apolipoprotein B is one of the proteins present in low-density lipoprotein (LDL), the bad cholesterol, and very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). VLDL primarily carries cholesterol from the liver to different tissues. Apolipoproteins drive this transport and help unload the cholesterol into the tissues. As the molecule reaches tissue sites, the fat gets transferred and the lipoprotein slowly changes form to become the LDL; apo B, meanwhile, stays the same.
Excess of LDL, if present in the body, gets deposited on the inner walls of blood vessels and narrow their lumen. This restricts the blood flow in the affected area, negatively affecting the surrounding tissues. LDL deposition also leads to hardening of blood vessel walls that then become prone to damage. When this process takes place in the blood vessels that supply the heart, it increases the risk of a heart attack.
Since apo B is so closely associated with LDL, the levels of apolipoprotein B in the blood are used to evaluate if you are at risk of a heart disorder.