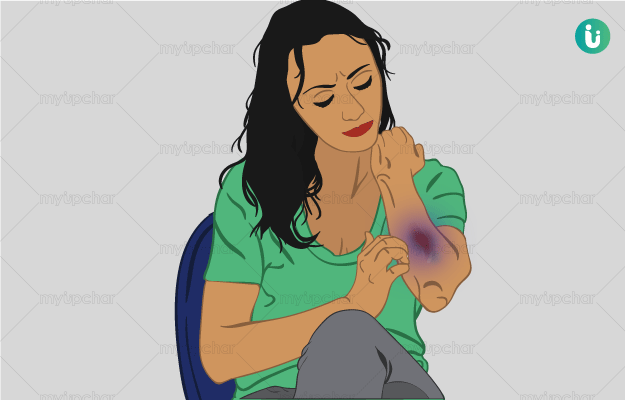
Bruising is a type of injury which is caused by rupturing of blood capillaries under the skin without breaking the epidermis. It is marked by the appearance of a blue-red patch on the skin, which does not fade when touched. Bruises mostly occur on the surface of the skin but in some cases, they can also be internal such as in bones or in muscles. Internal bruises are generally severe and can cause excessive pain and swelling. These bruises need special medical care and attention for quick recovery. On the other hand, topical bruises generally fade away on their own.

- हिं - हिंदी
- En - English
- Treatment
-
- Skin Issues
- Acne
- Fungal Infection
-
- Hair Problems
- Hair Growth
- Hair Dandruff
- Self-Analysis
-
- Chronic Diseases
- Diabetes
- Heart Care
- Weight Loss
- Sleep Support
- Liver Care
- Stress & Anxiety
- Our Brands
- Doctor Consultation
- Medicine A-Z
-
Health A-Z
-
- Treatments
- Home Remedies
- Herbs
- Surgery
- Lab Test
- Therapy
- First Aid
- Ayurveda
- Homeopathy
-
- Yoga And Fitness
- Fitness
- Yoga
- Weight Loss
- Weight Gain
-
- Other Topics
- Baby Names
- Beauty
- Healthy Foods
- Tips
- Health News
- Pet Health
- Men Health
- Medical Cannabis
- Login / Sign Up
 Doctors for Bruises
Doctors for Bruises  OTC Medicines for Bruises
OTC Medicines for Bruises