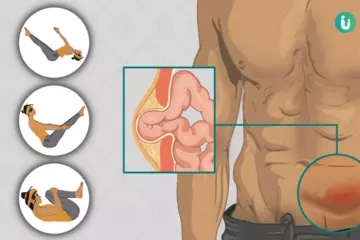
The stomach is a hollow organ—a kind of muscular pouch. The food that we swallow enters the stomach, where it is ground into tiny pieces by rhythmic contractions of the stomach muscles—these contractions cause a continuous churning. Once the food is ground properly, it is emptied from the stomach into the small intestine slowly—in a metered fashion.
Here's what happens in the metering process: while the part of the stomach which stores food becomes relaxed, another part which pushes the food into the small intestine gets pressurised. This helps the stomach to store and empty food at the same time. The metering process is controlled by the opening and closing of the pylorus: a muscular opening that joins the stomach into the small intestine.
When the stomach contractions are weak, the stomach cannot grind the food thoroughly and cannot empty it into the intestine properly, leading to gastroparesis.
Gastroparesis is a disease in which the stomach cannot empty itself of food in a normal fashion. This is a common condition in people who have had diabetes for a long time, but it may also occur in other situations. It's thought to be the result of a problem with the nerves and muscles that control how the stomach empties itself of food. (If these nerves are damaged, the muscles of your stomach may not work properly and the movement of food can slow down.)
The symptoms of gastroparesis may include heartburn, nausea and vomiting, and feeling full quickly when eating. Treatment may involve the use of medications to relieve the symptoms or surgery to correct the abnormalities.

 Doctors for Gastroparesis
Doctors for Gastroparesis