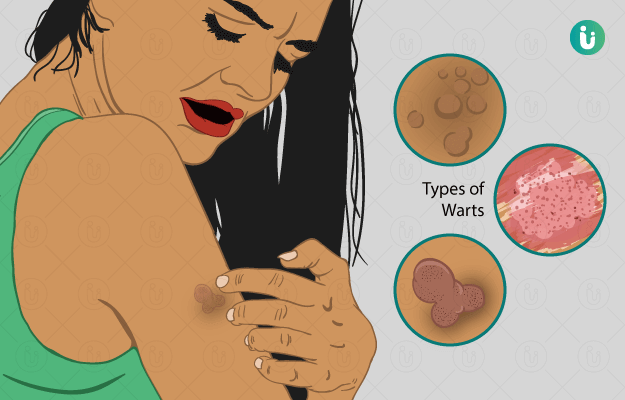
What is Human Papilloma Virus?
There are 120 types of the human papillomaviruses (HPVs) out of which about 40 are sexually transmitted.
HPV infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections and affects both males and females.
What are the main signs and symptoms?
- The symptoms of HPV infection vary depending on the type of virus that has entered the body.
- Most of the HPV virus strains cause warts. These are irregular elevations on the face, hands, neck, and genital area.
- HPV can also cause upper respiratory lesions which mainly occur in the tonsils, larynx, and throat.
- Some types of the virus also cause cervical cancer in females and oropharyngeal cancers. Cancer of the mouth or throat is also reported.
- When the virus causes cervical cancer, symptoms are not seen until the advanced stage.
What are its main causes?
- HPV usually enters the body through sexual contact with an infected person, as sex is the most common mode of transmission. (Read more: How to have safe sex)
- Having multiple sexual partners and oral sex increases the risk of contracting the infection.
- Patients with AIDS and other immune system diseases are more susceptible to HPV infection.
- It can also enter the body through an open wound, a cut, or exposed skin.
- Non-sexual transmission is by touching a wart on another person’s body.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
- In a physical examination, the doctor will examine the wart to arrive at a diagnosis. The medical and sexual history is also crucial.
- If HPV is suspected, a pap-smear test using a cotton swab run over the cervical cells is conducted for detecting abnormalities.
- The HPV virus that causes cervical cancer is often confirmed by the presence of viral DNA in the cervical cells through laboratory tests.
There is no treatment to eliminate the virus itself. It may remain latent or disappear without any intervention.
- For mild warts caused by HPV, the doctor may prescribe oral drugs as well as topical creams.
- If warts cannot be eliminated by medicines, surgical removal is carried out through lasers or cryotherapy.
- If HPV has caused cancer, extensive treatment, including chemotherapy or radiotherapy, is required.
- Although there are preventive vaccines available against cervical cancer caused by HPV, women need to take measures to prevent contracting the infection like using a condom during all sexual contact.

 Doctors for HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
Doctors for HPV (Human Papillomavirus)  OTC Medicines for HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
OTC Medicines for HPV (Human Papillomavirus)