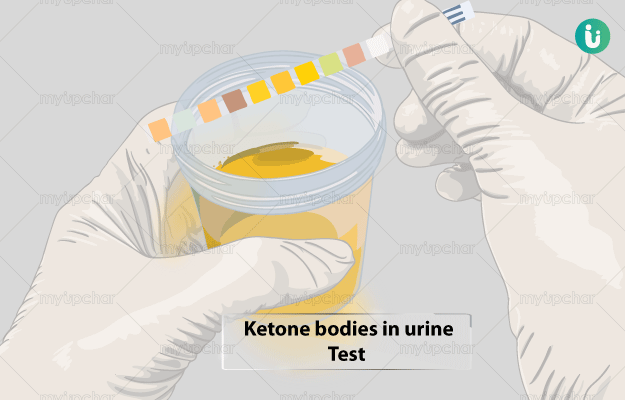
What is Ketone bodies in urine test?
Glucose is the primary source of energy for human body. It is transported to every cell of the body through a hormone called insulin. However, diabetic people, who have impaired or low insulin, cannot properly utilise glucose for energy production. Hence, their body starts to break down fats as an alternative source of energy.
Ketones are the breakdown products of fats. They are normally present in low amount in the urine. The presence of excess ketones in the urine leads to a condition called ketonuria. High levels of ketones in the body (Ketoacidosis) can result in serious illnesses or even death.
A ketone bodies urine test is used to check the amount of ketones that your body is releasing in urine. This test is assistive in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
Ketone levels in the body also go up in conditions of fasting and starvation. So, this test is also used for evaluating these conditions.
The alternative names of the test are ketones urine test, urine ketones, ketone bodies and ketone test.