What is Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) panel?
PCOD is a hormonal disorder that affects women in their reproductive age. It is associated with a group of symptoms including missing or irregular periods, excess facial or body hair (hirsutism) and infertility.
Though the exact cause of PCOD is still unknown, genetic factors, high levels of male hormones and insulin - the hormone responsible for controlling blood sugar levels - are considered to be the possible causes.
A PCOD panel helps diagnose Polycystic ovarian disease by checking the levels of these hormones along with all the hormones involved in their production and release. It includes the following tests— glucose, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinising hormone (LH), insulin, total testosterone, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin (PRL).
- DHEA-S: This male sex hormone is found in both men and women. It is produced by the adrenal glands and is converted into oestrogen and testosterone. It is important to the development of secondary sexual characteristics as you hit puberty. However, abnormally high levels of DHEA-S in women may indicate an overactive adrenal gland and lead to excessive body and facial hair, masculine features and menstrual problems.
- Glucose and insulin: Insulin promotes the storage of sugar in the liver, clearing it out from the blood. About 30%-40% of the women with PCOD experience insulin resistance leading to high glucose levels. To manage this, the pancreas produces more insulin, leading to elevated levels of insulin in the body. Studies suggest that insulin resistance in PCOS leads to increased production of male hormones from the adrenal gland, leading to increased masculine features in women.
- FSH: The pituitary gland, a pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain, secretes FSH in both men and women. This hormone is involved in maintaining the normal levels of testosterone and oestrogen in men and women, respectively. It also plays an important role in the sexual development of individuals and aids in the production of sperms in men and eggs in women. FSH levels in males rise at puberty and continue throughout life, whereas, in women, the levels vary at different stages of their menstrual cycle. Therefore, it is a useful tool in diagnosing conditions like PCOD in women.
- LH: LH is another hormone secreted by the pituitary gland. It is responsible for the development of ovarian follicles in females. LH also plays a vital role in ovulation and, therefore, can be considered an important hormone for the diagnosis of fertility-associated problems like PCOD.
- Total testosterone: Though it is primarily a male sex hormone, testosterone is found in both men and women. Total testosterone includes free testosterone in the blood and testosterone bound to proteins. Abnormal levels of testosterone help diagnose conditions related to sexual characteristics such as the development of male characteristics in women.
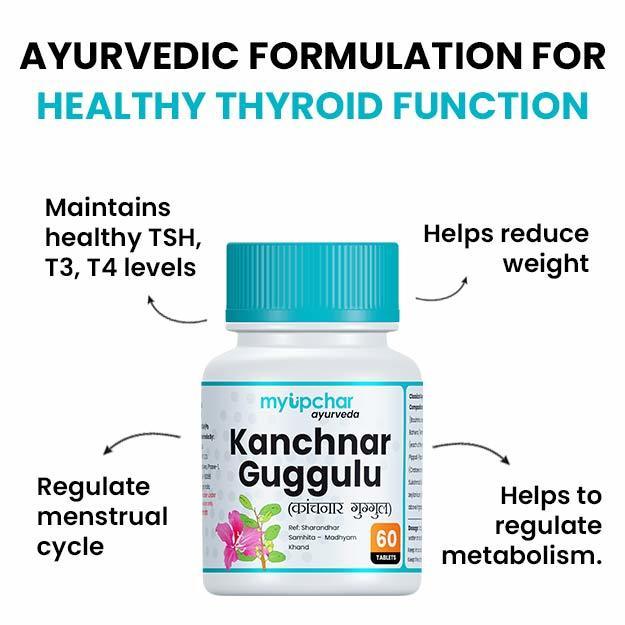
- TSH: The anterior pituitary gland secretes TSH as well, which aids in the regulation of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). Thyroid hormones are important for the metabolic functions, growth and development of the body. As the symptoms of abnormal levels of TSH are similar to PCOD, this test can help in ruling out TSH-related conditions and diagnosing PCOD.
- PRL: The pituitary gland is responsible for the production of PRL. PRL helps in metabolism, growth and sexual development. It stimulates milk production in lactating mothers and helps in regulating periods in nonpregnant women.