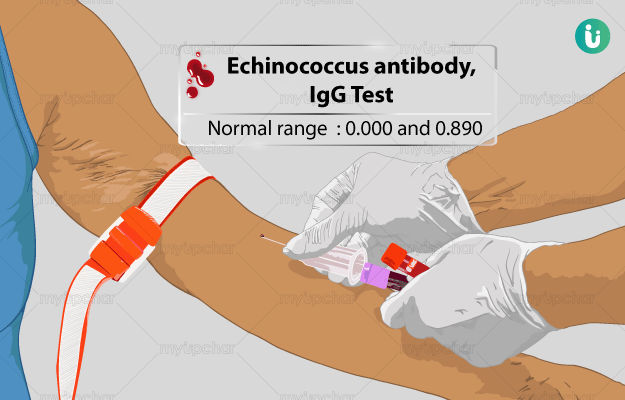
What is Echinococcus Antibody IgG test?
Echinococcus antibody test is used to measure IgG antibodies secreted by the body’s immune system against infections caused by the parasite Echinococcus or tapeworm.
Echinococcus infections are one of the most common parasitic infections in tropical areas. Animals such as dogs, sheep, pigs, cows, and goats host the immature form (larva) of the organism and release them through the stool into the soil.
Depending on the host animal, the two most common types of Echinococcus that affect humans are:
- Echinococcus granulosus: Causes Cystic echinococcosis. Dogs are the definitive host (the parasite reproduces in these). The larvae grow in lungs and liver
- Echinococcus multilocularis: Causes alveolar echinococcosis. Foxes are the definitive host. This disease is much rarer but fatal.
The larvae enter the human body through contaminated food or water and live in the form of hydatid cysts in various organs such as brain, liver and lungs. Hydatid cysts are complex structures that contain daughter larvae and cysts surrounded by a fluid. These cysts contain the echinococcus antigen, the part of the parasite that induces an immune response. Our body produces various types of antibodies against the Echinococcal antigen. These include IgG, IgM and IgE. Out of these IgG antibodies provide the most accurate diagnosis of an echinococcus infection and is hence the only antibody that is checked in an echinococcus antibody test.
The Echinococcus antibody test is an immunological study in which the antigen-antibody reaction is studied using different types of enzymes or chemicals. These chemicals are mixed with the antigens present in the test kit and produce fluorescence or specific colours if the antibodies in the blood sample react with the antigen in the test kit. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is based on this principle and is chiefly used to detect Echinococcus antibodies in the blood. Various other methods used to detect Echinococcus antibodies are latex agglutination, indirect haemagglutination, radioallergosorbent test and electrophoresis.