What is Micturating Cystourethrogram ( X-ray MCU)?
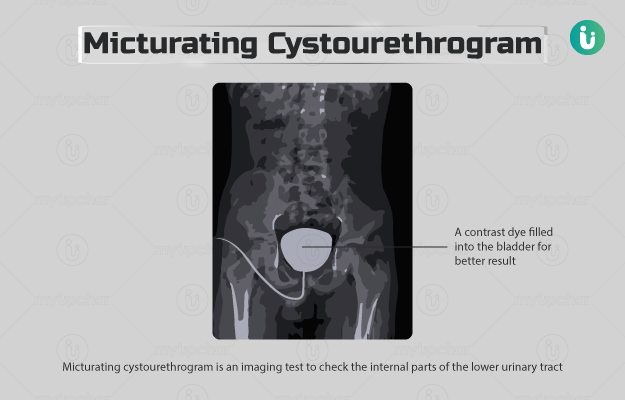
Micturating cystourethrogram (MCU), also called a voiding cystourethrogram, is an imaging test to check the internal parts of the lower urinary tract.
These parts include:
- Bladder (a bag that stores urine)
- Urethra (a tube that allows passage of urine outside the body)
In this test, x-ray images of the lower urinary tract are captured when the person is urinating (also known as micturition or voiding). A contrast dye usually filled into the bladder before taking the images. The dye helps to get more detailed images and hence better results.