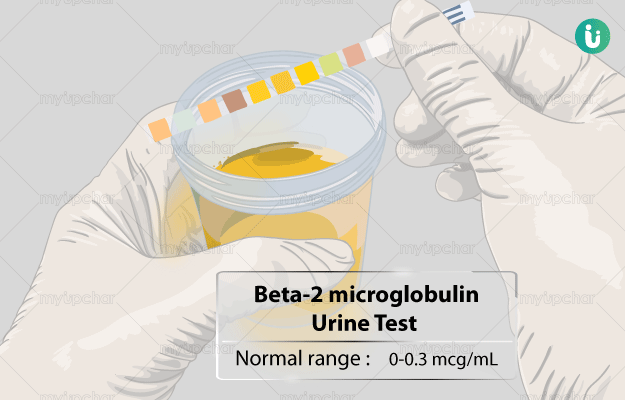
What is Beta-2 Microglobulin (B2M) Urine test?
Beta-2 microglobulin is a protein that is present on the surface of all nucleated cells (cells that contain a nucleus) and is periodically discarded into the bloodstream.
As the blood gets filtered in kidneys, most of the B2M is retained in the body. It passes through the glomeruli - the blood-filtering units of the kidney but gets reabsorbed in the renal proximal tubules (a segment of the kidney that reclaims the water, minerals, proteins and other filtered nutrients).
Generally, only minute concentrations of beta-2 microglobulin are present in the urine. However, if there is any damage to the renal tubules, the levels of beta-2 microglobulin in the urine increase. On the other hand, if the glomeruli are damaged, the beta-2 microglobulin cannot be filtered out, so the levels in the blood increase.
This test determines the amount of beta-2 microglobulin in your urine. It helps in detecting possible kidney damage.
Since it is released in blood by all types of cells, beta-2 microglobulin is also a tumour marker. Tumour markers are chemicals produced by cancer cells or by normal cells in response to cancer. A person with tumour or cancer would have a high amount of Beta-2 microglobulin in their urine. Though this test can’t diagnose cancer, it can tell you how serious your cancer is and how it may develop as it progresses.