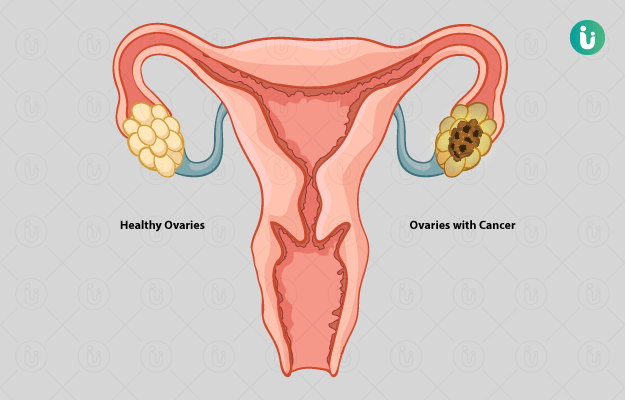
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Cancer in the tissues of the egg (ovum) producing organ (ovary) in a woman is called ovarian cancer. Ovarian tumours can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). It is one of the most dangerous gynaecological cancers and is commonly seen in older females.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Due to the slow development of ovarian cancer, it is often difficult to detect in the early stages. Some of the common signs and symptoms are :
- Menstrual irregularities or changes in flow and cycle.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Heartburn.
- Back and pelvic pain.
- Swelling in the pelvic region.
- Loss of appetite.
- Weigh loss.
- Nausea.
- Constipation.
- Bloating.
- Breathlessness.
- Fatigue.
- Frequent urination.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) mimics the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer.
What are the main causes?
The exact cause of most ovarian cancer is not clearly understood. Some of the common risk factors are :
- Inherited genetic mutations (for example, BRCA1/2, HNPCC).
- Women without children.
- Stress.
- Side effects of infertility treatment drugs.
- A family history of ovarian or breast cancer.
- Other possible risk factors include smoking, Western diet, obesity, using deodorants, talcum powder, environmental pollution, poverty and poor diet in childhood.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
For the diagnosis of ovarian cancer, doctors use various methods such as:
- Ultrasound of abdomen and pelvis
In the case of diseases of the ovaries, ultrasound is mostly preferred as the first test. - CT scan
It is used to detect larger tumours but is unable to detect the smaller ones. - MRI scan
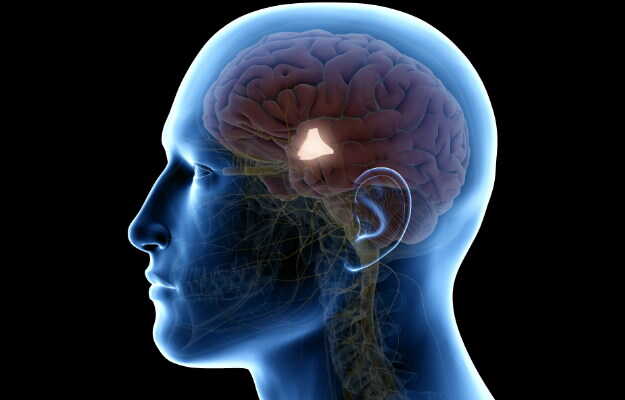
It helps in locating the spread of cancer to the brain or spinal cord. - Blood tests
CA-125 test is done to determine the level of CA-125 which is produced by the cancerous cells in the ovary.
After the cancer is diagnosed, it is treated by –
- Chemotherapy.
- Surgery.
- Radiation therapy.
There are also some complementary therapies like acupuncture, herbal medicine, meditation and yoga that may be used along with conventional treatment.

 Doctors for Ovarian Cancer
Doctors for Ovarian Cancer  OTC Medicines for Ovarian Cancer
OTC Medicines for Ovarian Cancer