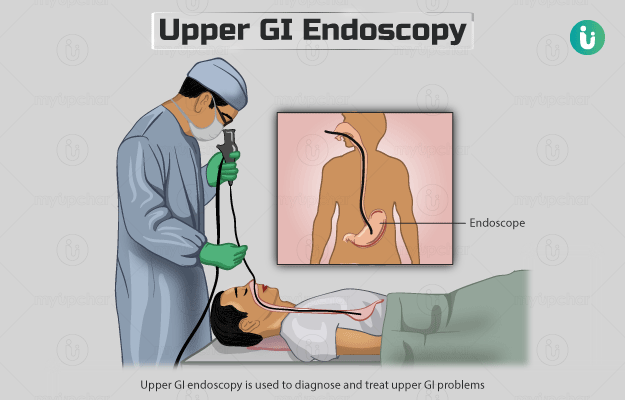
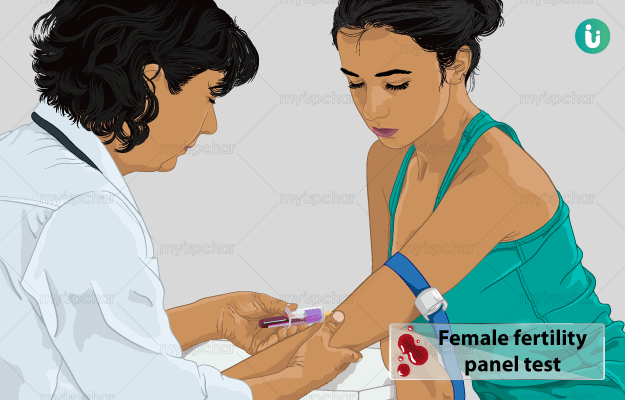
What is Phenytoin test?
Phenytoin is a drug that is used to treat epileptic seizures. It is effective against both: generalised tonic-clonic seizures (loss of consciousness and muscle jerking) and complex focal seizures (starts in one area of the brain and the person becomes confused or dazed)
Phenytoin is also used for seizures occurring during or after neurosurgery.
However, this drug has a narrow therapeutic window - the amount in which it shows efficacy. If the phenytoin doses are too high, it may lead to phenytoin toxicity, and if they are too low, the person may continue getting seizures.
Phenytoin is present in two forms in the body: Bound to albumin (90% of total phenytoin) and free form. Since bound albumin cannot reach the brain so only the free phenytoin is the active form.
This test is performed to determine the total amount of phenytoin in your blood so the right dose can be established.